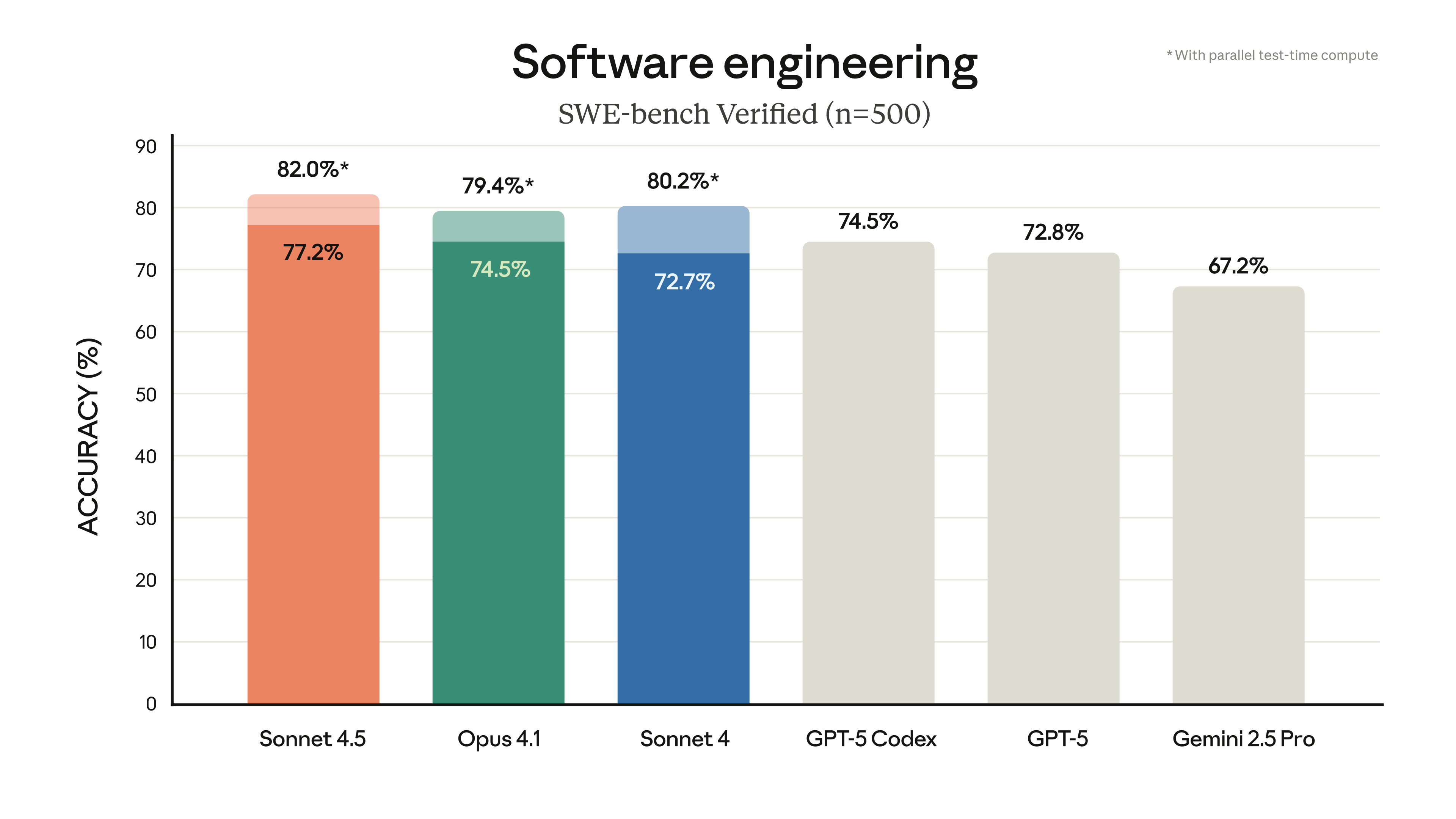
Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella Recently announced for Excel Introduces a built-in function:=COPILOT(). This update encapsulates the power of large-scale language modeling directly into cells, allowing the Excel This software with a history of nearly 40 years has once again become a distribution vehicle for cutting-edge technology. Unlike many AI functions implanted in the form of sidebar dialog, Microsoft has chosen to turn AI into a function that can be linked to data, behind which is a profound shift in product logic.
What is the =COPILOT() function?
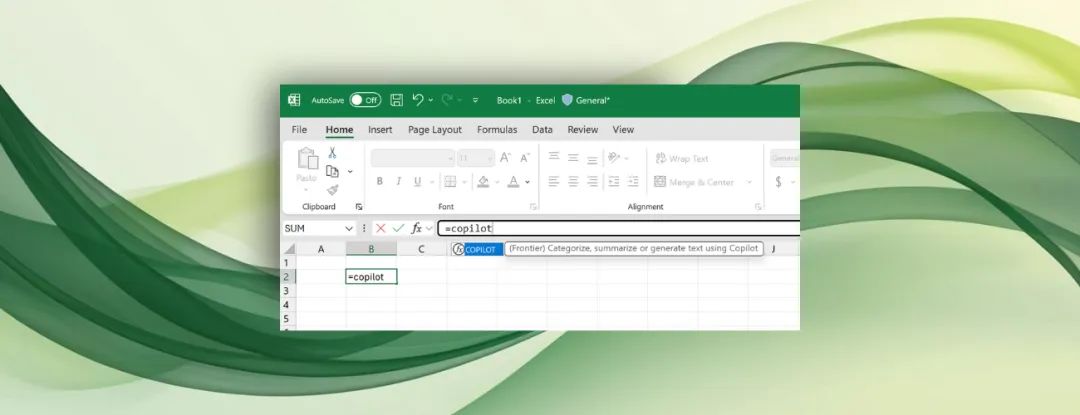
In a nutshell.=COPILOT() Allows users to invoke AI for calculations and analysis directly within a cell. The underlying syntax is structured as follows:
=COPILOT(prompt_part1, [context1], [prompt_part2], [context2], …)
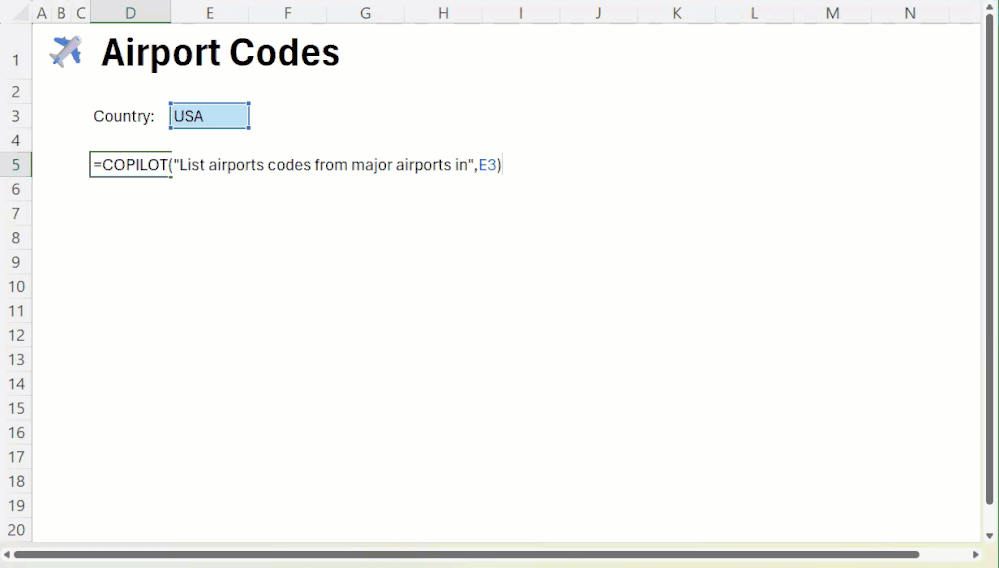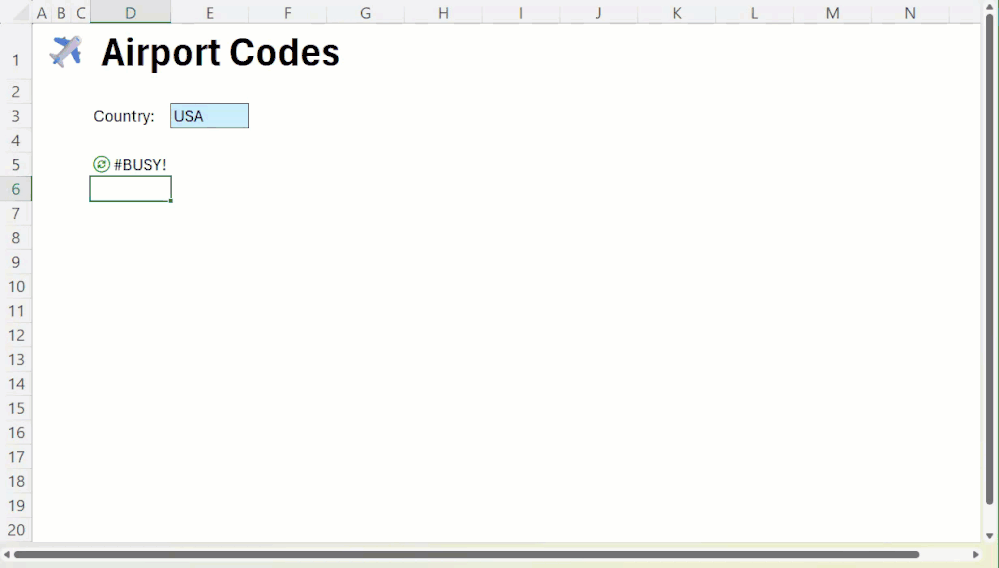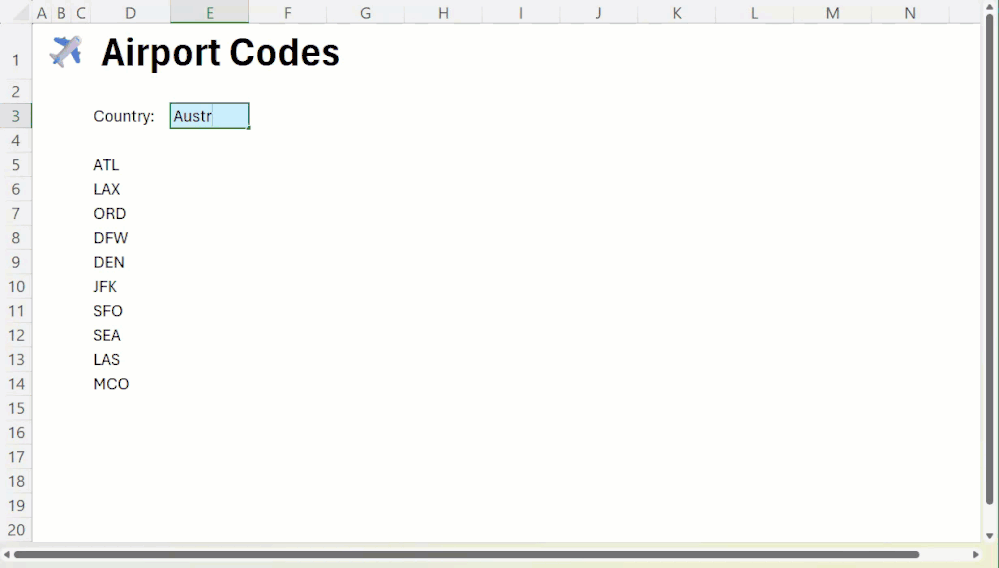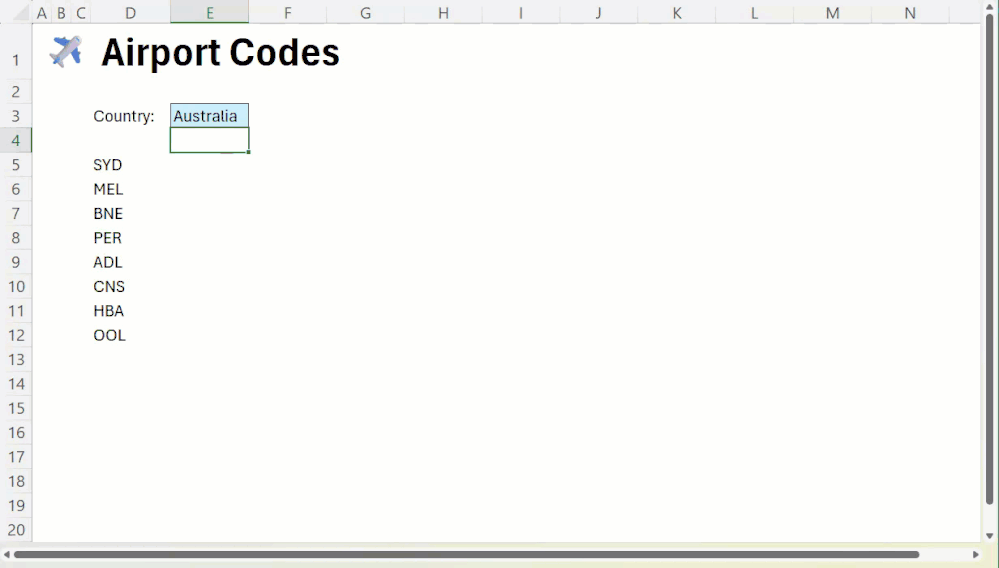
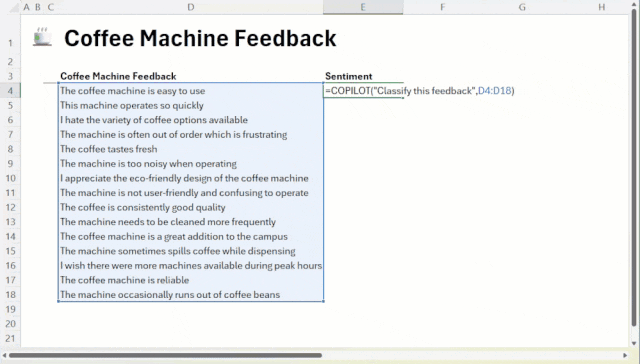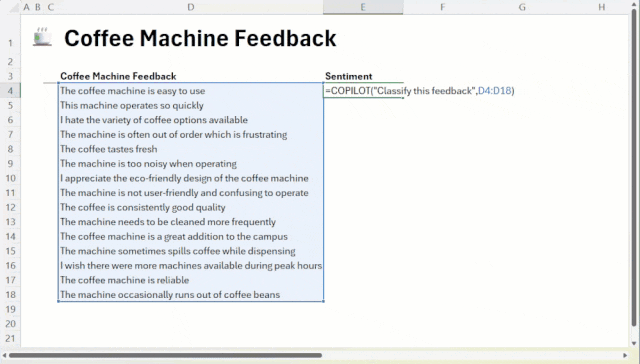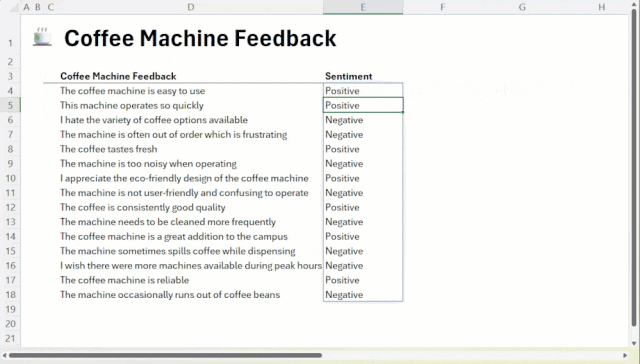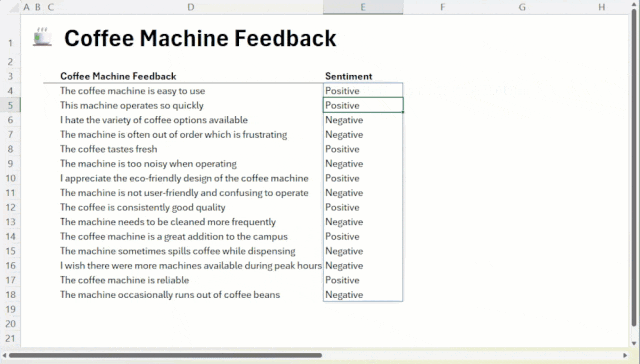
This function allows the user to pass commands and data ranges as parameters to the AI.For example, to make a sentiment judgment on customer comments in cells A1 through A10, simply enter:
=COPILOT("Perform sentiment analysis on these comments", A1:A10)
The AI will return a "positive" or "negative" judgment to the cell. The core advantage of this feature is that it works in conjunction with Excel The calculation engine is deeply integrated. When the source data (cells A1:A10) changes, the=COPILOT() The results of the function's calculations are updated automatically, eliminating the need for the user to manually perform a refresh or rerun the script.
Currently.=COPILOT() function mainly focuses on processing unstructured text data, its function covers the following scenarios:
- text analysis:: Extract keywords, classify emotions, and summarize textual content.
- Content generation: Generate product descriptions, SEO keywords or rewrite copy based on existing data.
- Data collation:: Extracting specific information from text, automatically formatting data.
Functional AI vs. Chatty AI
Making AI a cell function, rather than a standalone chat window, was Microsoft's most critical design decision for this update.Google Sheets A similar feature was previously introduced that allowed users to =GEMINI() function calls its Gemini Modeling. This signals that mainstream spreadsheet software is evolving in the same direction: making AI a native part of the data processing process.
The advantage of functional AI is its "automation" and "composability". Calculations are updated in real time as the data changes, and can be used like other Excel functions (e.g. IF、SUM), as it were, are nested within each other to build complex data processing workflows. This contrasts with chatty AI assistants that require users to repeatedly ask questions and copy and paste results.
This function is provided by Excel Labs Experimental functions in plugins LABS.GENERATIVEAI evolved and is now consolidated into Excel A core feature of the
Restrictions on use and version requirements
=COPILOT() It is still in early testing and there are some limitations to its use:
- Subscription Requirements:: Need to have
Microsoft 365 CopilotEnterprise Edition Subscription. - call frequency: Limit 100 calls per 10 minutes and 300 calls per hour.
- data access: Functions do not have direct access to live network data, all data to be processed must first be imported into a worksheet.
- data formatThe date returned by the : function is in text format, not in the
Excelof the native date format, which may require additional conversion.
This feature is currently only available for Beta Channel of users open.Windows Users need to upgrade to 2509 releases 19212.20000 or higher;Mac The user then needs to 16.101 releases 25081334 or higher.
For users who need to work with large amounts of text data, the=COPILOT() There is no doubt that efficiency can be greatly improved. However, it is worth noting that the "illusion" inherent in large-scale language models can be magnified in spreadsheet environments where precision is required. Users still need to be vigilant and validate AI-generated results, especially when working with business-critical data.