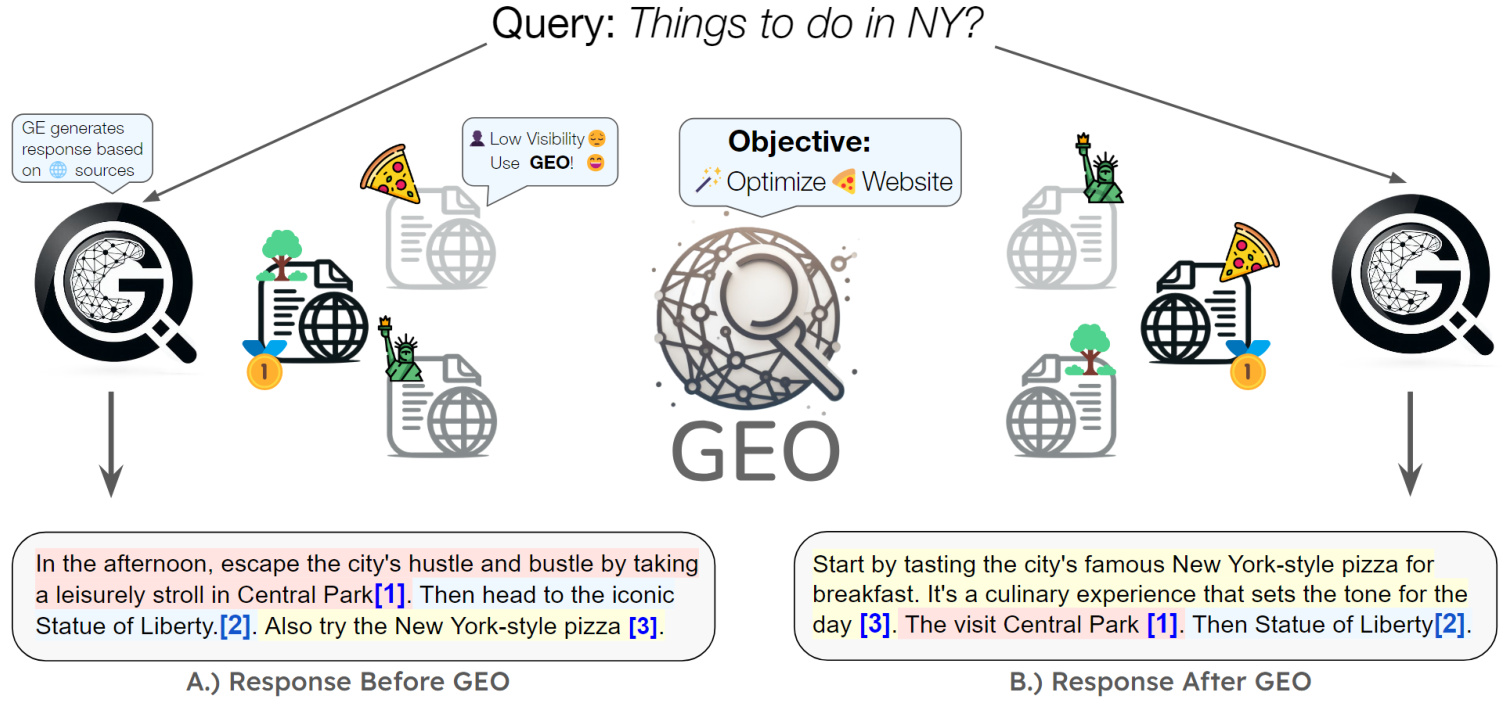
ベクトル埋め込みは、現在の検索拡張世代(RAG)アプリケーションの中核をなしている。ベクトル埋め込みは、データオブジェクト(テキスト、画像など)の意味情報をキャプチャし、それらを数値の配列として表現する。現在の生成AIアプリケーションでは、これらのベクトルEmbeddingは通常Embeddingモデルによって生成される。RAGアプリケーションに適したEmbeddingモデルを選択するには?全体として、それは特定のユースケースと特定の要件に依存します。次に、それぞれのステップを個別に見ていきましょう。
01.特定のユースケースを特定する
RAGの適用要件に基づき、以下の質問を検討する:
まず、ジェネリック・モデルは必要十分か?
第二に、特定のニーズがあるか。例えば、モダリティ(例:テキストまたは画像のみ、マルチモーダル埋め込みオプションについては正しいエンベデッドモデルの選び方")、特定の分野(法律、医学など)。
たいていの場合、希望するモードに対して一般的なモデルが選ばれるのが普通だ。
02.汎用モデルの選択
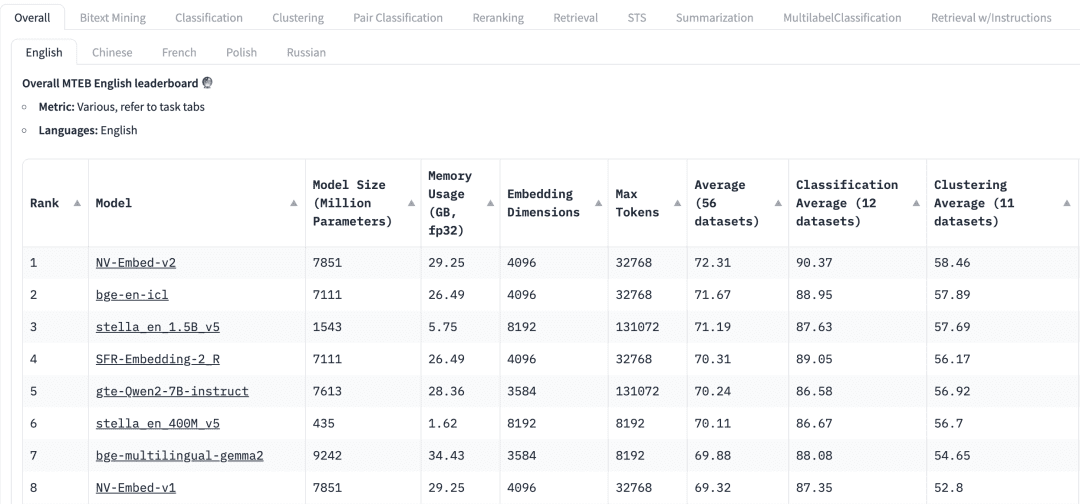
HuggingFaceのMassive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB)のリーダーボードには、現在のプロプライエタリおよびオープンソースの様々なテキスト埋め込みモデルがリストアップされています、埋め込み次元、トークンの最大数、そして検索や要約のようなタスクにおけるスコアなど、様々なメトリクスが表示されます。
RAGアプリケーションのエンベッディングモデルを選択する際には、以下の要素を考慮する必要があります:
マンデートMTEBリーダーボードのトップには、様々なタスクタブが表示されている。RAGアプリケーションでは、"Retrieve "タスクに集中する必要があるかもしれない。 Retrial このタブ。
多言語主義RAGが適用されたデータセットの言語に基づいて、対応する言語の埋め込みモデルを選択する。
スコア特定のベンチマークデータセット、または複数のベンチマークデータセットに対するモデルのパフォーマンスを示します。タスクによって、異なる評価指標が使用されます。通常、これらの評価指標は 0 から 1 までの値をとり、値が大きいほど性能が優れていることを示します。
モデルサイズとメモリ使用量これらの指標は、モデルの実行に必要な計算リソースを示している。検索性能はモデル・サイズとともに向上しますが、モデル・サイズもレイテンシに直接影響することに注意することが重要です。さらに、大きなモデルはオーバーフィットして汎化性能が低くなり、本番でのパフォーマンスが低下する可能性があります。したがって、実稼働環境におけるパフォーマンスとレイテンシのバランスを追求する必要があります。一般的には、まず小さくて軽量なモデルから始めて、RAGアプリケーションを迅速に構築することができる。アプリケーションの基礎となるプロセスが適切に動作するようになったら、アプリケーションをさらに最適化するために、より大規模で高性能なモデルに切り替えることができます。
埋め込み寸法これはEmbeddingベクトルの長さである。Embeddingの次元を大きくすれば、データのより詳細な情報を捉えることができますが、その結果は必ずしも最適とは限りません。例えば、文書データに8192次元が本当に必要でしょうか?おそらくそうではないでしょう。一方、Embeddingの次元を小さくすれば、より高速な推論が可能になり、ストレージやメモリの面でも効率的です。したがって、データ内容の把握と実行効率のバランスをうまくとる必要がある。
トークンの最大数は1つのEmbeddingの最大トークン数を示します。一般的なRAGアプリケーションでは、Embeddingに適したチャンクサイズは通常1段落で、その場合、最大トークン数512のEmbeddingモデルで十分です。しかし、特殊なケースでは、より長いテキストを扱うために、より多くのトークン数を持つモデルが必要になることがあります。
03.RAGアプリケーションにおけるモデルの評価
MTEBのリーダーボードから一般的なモデルを見つけることはできるが、その結果は慎重に扱う必要がある。これらの結果はモデルによる自己申告であることを念頭に置くと、モデルによっては、MTEBデータセットをトレーニングデータに含めている可能性があるため、パフォーマンスを誇張したスコアを出している可能性があります。また、モデルがベンチマークに使用するデータセットが、我々のアプリケーションで使用するデータを正確に表していない可能性もある。したがって、私たちは独自のデータセットでエンベッディング・モデルを評価する必要があります。
3.1 データセット
RAGアプリケーションで使用するデータから、小さなタグ付きデータセットを生成することができる。次のデータセットを例にしてみよう。
| Language | Description |
|---|---|
| C/C++ | A general-purpose programming language known for its performance and efficiency. It provides low-level memory manipulation capabilities and is widely used in system/software development, game development, and applications requiring high performance. |
| Java | A versatile, object-oriented programming language designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is widely used for building enterprise-scale applications, mobile applications (especially Android), and web applications due to its portability and robustness. |
| Python | A high-level, interpreted programming language known for its readability and simplicity. It supports multiple programming paradigms and is widely used in web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, scientific computing, and automation. |
| JavaScript | A high-level, dynamic programming language primarily used for creating interactive and dynamic content on the web. It is an essential technology for front-end web development and is increasingly used on the server-side with environments like Node.js. |
| C# | A modern, object-oriented programming language developed by Microsoft. It is used for developing a wide range of applications, including web, desktop, mobile, and games, particularly within the Microsoft ecosystem. |
| SQL | A domain-specific language used in programming and managing relational databases. It is essential for querying, updating, and managing data in databases, and is widely used in data analysis and business intelligence. |
| PHP | A server-side scripting language designed primarily for web development. It is embedded into HTML and is widely used for building dynamic web pages and applications, with a strong presence in content management systems like WordPress. |
| Golang | A statically typed, compiled programming language designed by Google. Known for its simplicity and efficiency, it is used for building scalable and high-performance applications, particularly in cloud services and distributed systems. |
| Rust | A systems programming language focused on safety and concurrency. It provides memory safety without using a garbage collector and is used for building reliable and efficient software, particularly in systems programming and web assembly. |
3.2 エンベディングの作成
次にpymilvus[model]上記のデータセットに対して、対応するベクトルEmbeddingが生成される。 pymilvus[model] 使用方法については、https://milvus.io/blog/introducing-pymilvus-integrations-with-embedding-models.md を参照。
def gen_embedding(model_name): openai_ef = model.dense.OpenAIEmbeddingFunction( model_name=model_name, api_key=os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] ) docs_embeddings = openai_ef.encode_documents(df['description'].tolist()) return docs_embeddings, openai_ef
そして、生成されたエンベディングはミルヴァスのコレクションに預けられる。
def save_embedding(docs_embeddings, collection_name, dim):
data = [
{"id": i, "vector": docs_embeddings[i].data, "text": row.language}
for i, row in df.iterrows()
]
if milvus_client.has_collection(collection_name=collection_name):
milvus_client.drop_collection(collection_name=collection_name)
milvus_client.create_collection(collection_name=collection_name, dimension=dim)
res = milvus_client.insert(collection_name=collection_name, data=data)
3.3 クエリー
我々は、ベクトル埋め込みを容易に呼び出すためのクエリー関数を定義する。
def query_results(query, collection_name, openai_ef):
query_embeddings = openai_ef.encode_queries(query)
res = milvus_client.search(
collection_name=collection_name,
data=query_embeddings,
limit=4,
output_fields=["text"],
)
result = {}
for items in res:
for item in items:
result[item.get("entity").get("text")] = item.get('distance')
return result
3.4 埋め込みモデルの性能評価
OpenAIの2つのEmbeddingモデルを使用しています。text-embedding-3-small 和 text-embedding-3-large以下の2つのクエリについて比較する。accuracy、recall、MRR、MAPなど多くの評価指標がある。ここでは、accuracyとrecallを使用する。
精度(Precision) 検索結果における、本当に関連性のあるコンテンツの割合、つまり、返された検索結果のうち、いくつが検索クエリに関連しているかを評価する。
Precision = TP / (TP + FP)
この場合、TP(True Positives)はクエリに本当に関連するもので、FP(False Positives)は検索結果に関連しないものを指す。
Recallは、データセット全体から検索に成功した関連コンテンツの量を評価する。
Recall = TP / (TP + FN)
偽陰性(False Negatives:FN)とは、最終的な結果セットに含まれないすべての関連項目を指す。
お問い合わせ1:auto garbage collection
関連項目:Java、Python、JavaScript、Golang
| Rank | text-embedding-3-small | text-embedding-3-large |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | サビ | サビ |
| 2 | C/C++ | C/C++ |
| 3 | ✅ ゴラン | ジャワ |
| 4 | ジャワ | ✅ ゴラン |
| Precision | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Recall | 0.50 | 0.50 |
問い合わせ2:suite for web backend server development
関連項目:Java、JavaScript、PHP、Python(回答は主観的判断を含む)
| Rank | text-embedding-3-small | text-embedding-3-large |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PHP | JavaScript |
| 2 | ジャワ | ジャワ |
| 3 | JavaScript | PHP |
| 4 | C# | パイソン |
| Precision | 0.75 | 1.0 |
| Recall | 0.75 | 1.0 |
これらの2つのクエリにおいて、精度と再現率で2つの埋め込みモデルを比較した。 text-embedding-3-small 和 text-embedding-3-large Embeddingモデルは出発点として使うことができる。これを出発点として、データセットのデータオブジェクトの数を増やし、クエリの数を増やすことで、Embeddingモデルをより効果的に評価することができる。
04.概要
検索拡張生成(RAG)アプリケーションでは、適切なベクトル埋め込みモデルの選択が重要である。本論文では、実際のビジネス要件からMTEBから汎用モデルを選択した後、ビジネス固有のデータセットに基づいてモデルをテストするために精度と想起を使用し、最適なEmbeddingモデルを選択することで、RAGアプリケーションの想起精度を効果的に向上させることを示す。
完全なコードはダウンロード可能