01.コンテキスト
RAGアプリケーションの開発では、最初のステップは、ドキュメントをチャンキングすることです、効率的なドキュメントのチャンキングは、効果的にその後のリコールコンテンツの精度を向上させることができます。どのように効率的にチャンキングするかは議論のホットトピックであり、固定サイズチャンキング、ランダムサイズチャンキング、スライディングウィンドウリサンプリング、再帰的チャンキング、意味チャンキングの内容に基づいて、他の方法などがあります。Jina AIが提案したLate Chunkingは、チャンキング問題を別の視点から扱っている。
02.レイト・チャンキングとは?
従来のチャンキングでは、長い文書を扱う場合、文書内の長距離の文脈依存関係が失われる可能性があり、これは情報検索と理解のための大きな落とし穴である。つまり、重要な情報が複数のテキストブロックに散らばっている場合、文脈から外れたテキストチャンキング断片は本来の意味を失い、その後の想起が悪くなる可能性が高い。
Milvus 2.4.13のリリースノートを例にとると、以下のように2つのドキュメントブロックに分かれている場合、次のようなクエリが必要です。Milvus 2.4.13有哪些新功能?この時点で、Embeddingモデルがこれらの参照をエンティティに正しくリンクすることは困難であり、質の低いEmbeddingとなる。
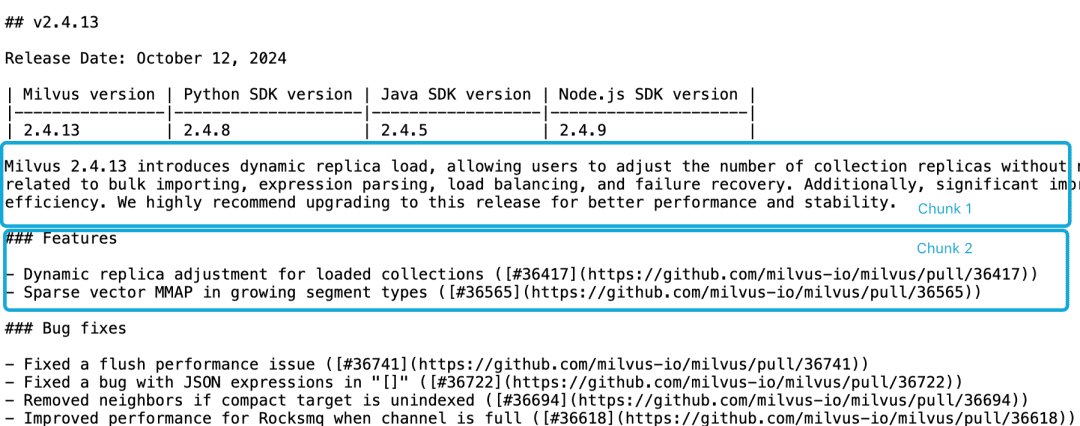
LLMは、機能記述がバージョン情報と同じチャンクにないことと、より大きな文脈文書がないことから、このような相関問題を解決することが困難である。スライディングウィンドウの再サンプリング、オーバーラップするコンテキストウィンドウの長さ、複数の文書のスキャンなど、この問題を軽減しようとするヒューリスティックは数多くあるが、他のヒューリスティックと同様、これらの方法はヒット&ミスである。
従来のチャンキングでは、まずチャンキングを行い、次にエンベッディング・モデルを通すというプレ・チャンキング戦略を採用している。テキストはまず、文、段落、あらかじめ設定された最大長などのパラメータに基づいてカットされる。次に、埋め込みモデルが、平均プーリングや、チャンクを1つずつ処理する方法によって、チャンクを1つずつ処理する。 token レイト・チャンキングとは、まずエンベッディング・モデルを経てからチャンキングすることである(これがレイトの意味である)。一方、レイト・チャンキングとは、チャンキングの前にエンベッディング・モデルを通過することである(これがレイトの意味であり、まずベクトル化してからチャンキングする)。 transformer このレイヤーはテキスト全体に適用され、豊富な文脈情報を含む各トークンのベクトル表現シーケンスを生成する。そして、これらのトークンのベクトル列を均等にプールし、テキスト全体の文脈を考慮した最終的なブロック埋め込みを得る。
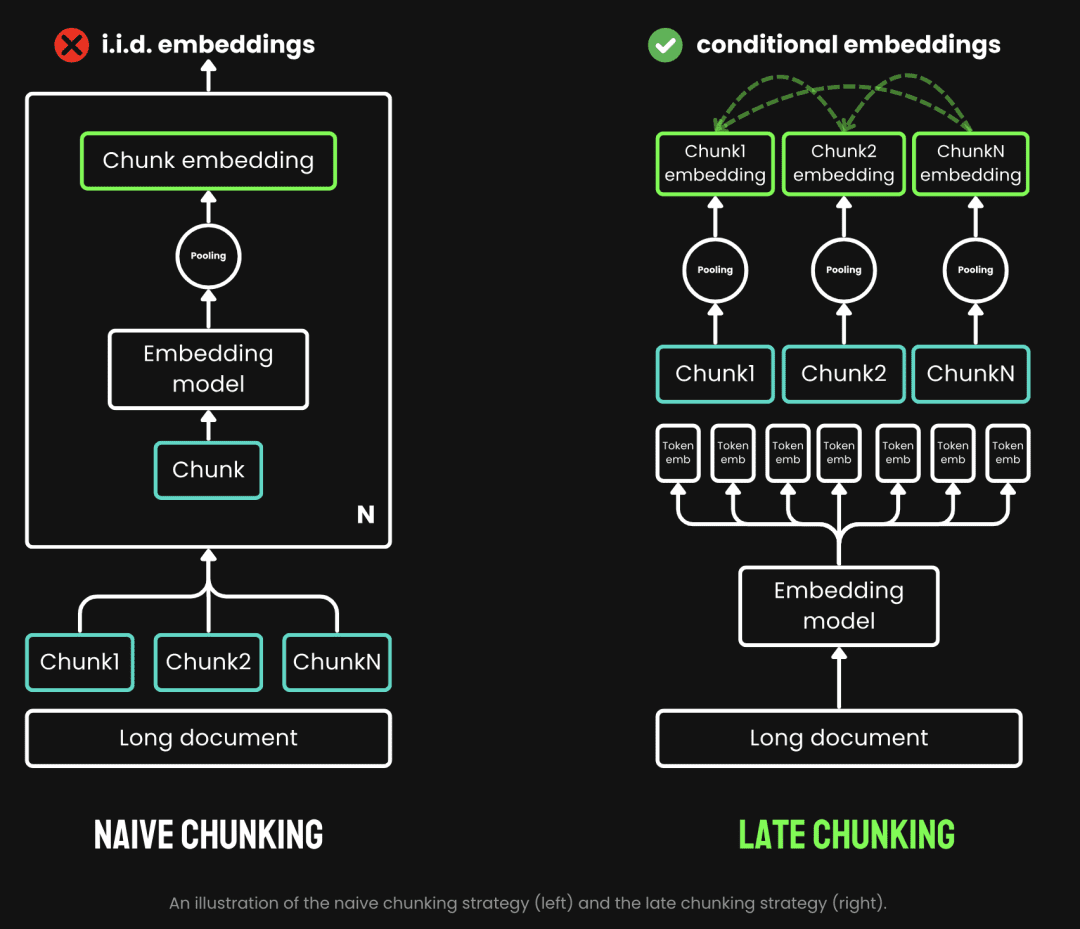
(画像出典:https://jina.ai/news/late-chunking-in-long-context-embedding-models/)
レイト・チャンキングは、各ブロックがより多くの文脈情報をエンコードするブロックEmbeddingを生成し、エンコードの品質と精度を向上させる。以下のような長いコンテキストをサポートすることで、長いコンテキストのEmbeddingモデルをサポートすることができる。 jina-embeddings-v2-base-en最大8192トークン(A4用紙10ページ分)のテキストを処理でき、ほとんどの長文テキストの文脈要件を基本的に満たしている。
まとめると、RAGアプリケーションにおけるレイト・チャンキングの利点がわかる:
- 精度の向上: コンテキスト情報を保持することで、レイト・チャンキングは単純なチャンキングよりもクエリに対してより関連性の高いコンテンツを返します。
- 効率的なLLMの呼び出し:レイト・チャンキングは、より少なく、より関連性の高いチャンクを返すため、LLMに渡されるテキストの量を減らす。
03.レイト・チャンキングのテスト
3.1.後期チャンキング・ベースの実装
チャンクの内容とチャンクのマーキング情報span_annotation(つまり、チャンクのマーキングの開始と終了)を返す。
def sentence_chunker(document, batch_size=10000):
nlp = spacy.blank("en")
nlp.add_pipe("sentencizer", config={"punct_chars": None})
doc = nlp(document)
docs = []
for i in range(0, len(document), batch_size):
batch = document[i : i + batch_size]
docs.append(nlp(batch))
doc = Doc.from_docs(docs)
span_annotations = []
chunks = []
for i, sent in enumerate(doc.sents):
span_annotations.append((sent.start, sent.end))
chunks.append(sent.text)
return chunks, span_annotations
関数 document_to_token_embeddings は、モデル jinaai/jina-embeddings-v2-base-en モデルだけでなく、文書全体の埋め込みを返すトークナイザーもあります。
def document_to_token_embeddings(model, tokenizer, document, batch_size=4096): tokenized_document = tokenizer(document, return_tensors="pt") tokens = tokenized_document.tokens() outputs = [] for i in range(0, len(tokens), batch_size): start = i end = min(i + batch_size, len(tokens)) batch_inputs = {k: v[:, start:end] for k, v in tokenized_document.items()} with torch.no_grad(): model_output = model(**batch_inputs) outputs.append(model_output.last_hidden_state) model_output = torch.cat(outputs, dim=1) return model_output
関数late_chunkingは、元のチャンクのマークアップ情報span_annotationと同様に、文書全体のEmbeddingをチャンクする。
def late_chunking(token_embeddings, span_annotation, max_length=None): outputs = [] for embeddings, annotations in zip(token_embeddings, span_annotation): if ( max_length is not None ): annotations = [ (start, min(end, max_length - 1)) for (start, end) in annotations if start < (max_length - 1) ] pooled_embeddings = [] for start, end in annotations: if (end - start) >= 1: pooled_embeddings.append( embeddings[start:end].sum(dim=0) / (end - start) ) pooled_embeddings = [ embedding.detach().cpu().numpy() for embedding in pooled_embeddings ] outputs.append(pooled_embeddings) return outputs
モデルを使用する場合jinaai/jina-embeddings-v2-base-enレイト・チャンキングを行う
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('jinaai/jina-embeddings-v2-base-en', trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained('jinaai/jina-embeddings-v2-base-en', trust_remote_code=True)
# First chunk the text as normal, to obtain the beginning and end points of the chunks.
chunks, span_annotations = sentence_chunker(document)
# Then embed the full document.
token_embeddings = document_to_token_embeddings(model, tokenizer, document)
# Then perform the late chunking
chunk_embeddings = late_chunking(token_embeddings, [span_annotations])[0]
3.2.従来の埋め込み方法との比較
milvus 2.4.13のリリースノートを例にとってみよう。
Milvus 2.4.13 introduces dynamic replica load, allowing users to adjust the number of collection replicas without needing to release and reload the collection.
This version also addresses several critical bugs related to bulk importing, expression parsing, load balancing, and failure recovery.
Additionally, significant improvements have been made to MMAP resource usage and import performance, enhancing overall system efficiency.
We highly recommend upgrading to this release for better performance and stability.
伝統的なEmbedding、すなわちチャンキングの後にEmbeddingを行う方法と、Late ChunkingアプローチのEmbedding、すなわちEmbeddingの後にチャンキングを行う方法がそれぞれ実行される。次に milvus 2.4.13 これら2つのエンベッディング・アプローチの結果をそれぞれ比較してみよう。
cos_sim = lambda x, y: np.dot(x, y) / (np.linalg.norm(x) * np.linalg.norm(y))
milvus_embedding = model.encode('milvus 2.4.13')
for chunk, late_chunking_embedding, traditional_embedding in zip(chunks, chunk_embeddings, embeddings_traditional_chunking):
print(f'similarity_late_chunking("milvus 2.4.13", "{chunk}")')
print('late_chunking: ', cos_sim(milvus_embedding, late_chunking_embedding))
print(f'similarity_traditional("milvus 2.4.13", "{chunk}")')
print('traditional_chunking: ', cos_sim(milvus_embedding, traditional_embeddings))
この結果から、単語 milvus 2.4.13 チャンク化された文書とレイト・チャンキングの結果の類似性は、従来のエンベッディングよりも高い。 milvus 2.4.13 という情報は、その後のテキスト比較における類似性を著しく向上させる。
similarity_late_chunking("milvus 2.4.13", "Milvus 2.4.13 introduces dynamic replica load, allowing users to adjust the number of collection replicas without needing to release and reload the collection.")
late_chunking: 0.8785206
similarity_traditional("milvus 2.4.13", "Milvus 2.4.13 introduces dynamic replica load, allowing users to adjust the number of collection replicas without needing to release and reload the collection.")
traditional_chunking: 0.8354263
similarity_late_chunking("milvus 2.4.13", "This version also addresses several critical bugs related to bulk importing, expression parsing, load balancing, and failure recovery.")
late_chunking: 0.84828955
similarity_traditional("milvus 2.4.13", "This version also addresses several critical bugs related to bulk importing, expression parsing, load balancing, and failure recovery.")
traditional_chunking: 0.7222632
similarity_late_chunking("milvus 2.4.13", "Additionally, significant improvements have been made to MMAP resource usage and import performance, enhancing overall system efficiency.")
late_chunking: 0.84942204
similarity_traditional("milvus 2.4.13", "Additionally, significant improvements have been made to MMAP resource usage and import performance, enhancing overall system efficiency.")
traditional_chunking: 0.6907381
similarity_late_chunking("milvus 2.4.13", "We highly recommend upgrading to this release for better performance and stability.")
late_chunking: 0.85431844
similarity_traditional("milvus 2.4.13", "We highly recommend upgrading to this release for better performance and stability.")
traditional_chunking: 0.71859795
3.3. Milvusにおける後期チャンキングのテスト
後期チャンキング・データのMilvusへのインポート
batch_data=[]
for i in range(len(chunks)):
data = {
"content": chunks[i],
"embedding": chunk_embeddings[i].tolist(),
}
batch_data.append(data)
res = client.insert(
collection_name=collection,
data=batch_data,
)
クエリーテスト
ここでは、コサイン類似度クエリー法と、Milvusネイティブクエリー法をそれぞれLate Chunking用に定義する。
def late_chunking_query_by_milvus(query, top_k = 3):
query_vector = model(**tokenizer(query, return_tensors="pt")).last_hidden_state.mean(1).detach().cpu().numpy().flatten()
res = client.search(
collection_name=collection,
data=[query_vector.tolist()],
limit=top_k,
output_fields=["id", "content"],
)
return [item.get("entity").get("content") for items in res for item in items]
def late_chunking_query_by_cosine_sim(query, k = 3):
cos_sim = lambda x, y: np.dot(x, y) / (np.linalg.norm(x) * np.linalg.norm(y))
query_vector = model(**tokenizer(query, return_tensors="pt")).last_hidden_state.mean(1).detach().cpu().numpy().flatten()
results = np.empty(len(chunk_embeddings))
for i, (chunk, embedding) in enumerate(zip(chunks, chunk_embeddings)):
results[i] = cos_sim(query_vector, embedding)
results_order = results.argsort()[::-1]
return np.array(chunks)[results_order].tolist()[:k]
この結果から、2つの方法は同じ内容を返し、MilvusにおけるLate Chunkingのクエリの結果が正確であることを示している。
> late_chunking_query_by_milvus("What are new features in milvus 2.4.13", 3)
['nn### Featuresnn- Dynamic replica adjustment for loaded collections ([#36417](https://github.com/milvus-io/milvus/pull/36417))n- Sparse vector MMAP in growing segment types ([#36565](https://github.com/milvus-io/milvus/pull/36565))...
> late_chunking_query_by_cosine_sim("What are new features in milvus 2.4.13", 3)
['nn### Featuresnn- Dynamic replica adjustment for loaded collections ([#36417](https://github.com/milvus-io/milvus/pull/36417))n- Sparse vector MMAP in growing segment types ([#36565](https://github.com/milvus-io/milvus/pull/36565))...
04.概要
我々は、レイト・チャンキングが生まれた背景、基本的なコンセプト、基本的な実装を紹介し、ミブラスでテストすることにより、レイト・チャンキングがうまく機能することを発見した。全体として、精度、効率、実装の容易さの組み合わせにより、レイト・チャンキングはRAGアプリケーションにとって効果的なアプローチとなっている。
参考文档:
- https://stackoverflow.blog/2024/06/06/breaking-up-is-hard-to-do-chunking-in-rag-applications
- https://jina.ai/news/late-chunking-in-long-context-embedding-models/
- https://jina.ai/news/what-late-chunking-really-is-and-what-its-not-part-ii/
サンプルコード:
リンク: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1cYNfZTTXd7RwjnjPFylReg?pwd=1234 抽出コード: 1234 AWSのg4dn.xlargeマシンで動作するコード