OpenClaw (formerly known as Moltbot/ClawdBot) has recently attracted a lot of attention in the developer community. As a main “Local-First” (Local-First) open source Agent framework, it has become a strong glue connecting the big model and the real business flow with excellent autonomous execution capability and plug-in extensibility.
For many developers who want to try it out, installing it directly on local devices may face problems such as environmental pollution and complicated permission management, while purchasing a cloud server is an additional expense. In this article, we will introduce aTotally free, secure and no public IP required!The deployment solution: build a temporary sandbox using GitHub Codespaces, combine it with the long connection mode of Flying Book (Lark), and run through a set of your own AI intelligences in 15 minutes.

Core Concept Analysis
GitHub Codespaces: a standardized development machine in the cloud
GitHub Codespaces is a cloud-based development environment based on Docker container technology. It provides developers with a standard container pre-installed with Linux (Ubuntu), VS Code Server and common runtimes.
- dominance: No need to configure the local environment, the browser is ready to use; the environment is isolated and does not contaminate the local system.
- characterizationFree users have 60 hours of free credit per month (enough for testing). Note that Codespaces hasad hocIt is suitable for development and debugging rather than hosting in production environments, and will automatically sleep after about 30 minutes (default) to 4 hours of idle time.
OpenClaw Gateway: The Control Hub for Intelligent Bodies
OpenClaw adopts the Gateway-Node architecture, where the Gateway acts as the control plane, responsible for managing sessions, authentication, channels and task distribution. In this deployment, the Gateway will run in the Codespaces container and actively establish long connections to the Flying Book server via the WebSocket protocol, thus avoiding the traditional WebHook model's dependence on fixed IPs on the public network.
preliminary
Before you start, make sure you have the following list:
- GitHub account: Used to create Codespaces instances.
- Flybook/Lark account: Have the authority to create enterprise self-built applications (Custom App).
- Basic terminal operation ability: Be able to understand and execute Linux Shell commands.
Phase 1: Building a Cloud Runtime Environment
1. Creating Codespaces instances
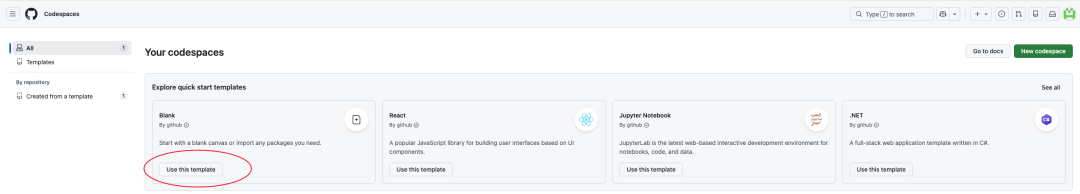
Visit the GitHub Codespaces homepage and click on the left navigation bar of the “New codespace” or select “Blank” template to initialize a pristine Linux environment.
option “Blank” After the template, the system will automatically pull the image and start the container.
After waiting for the loading to complete, the Terminal console will appear at the bottom of the interface. All subsequent interactions will be done here.
2. Installation of OpenClaw core components
Execute the officially provided one-click installation script in the terminal. The script will automatically detect the system architecture (x86_64/ARM), download the corresponding version of the binary and configure environment variables.
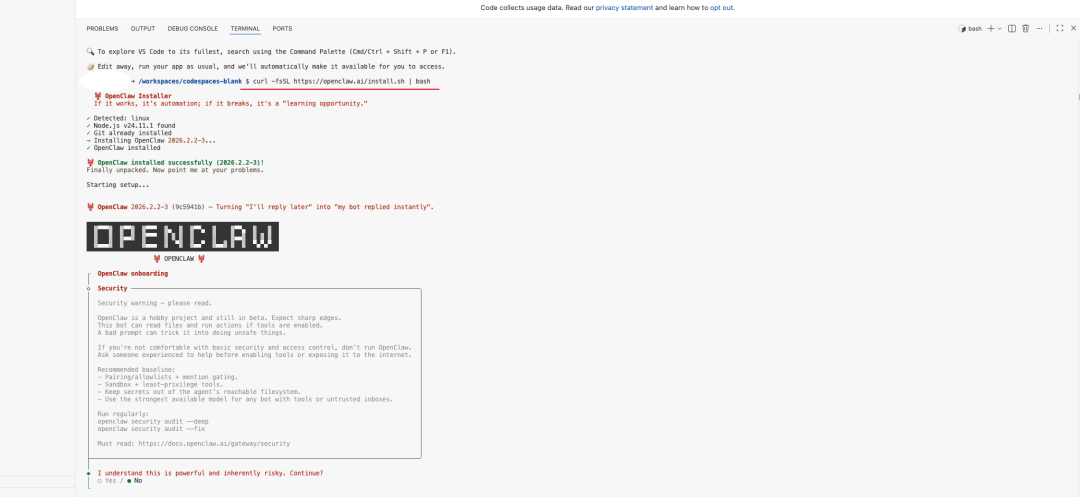
curl -fsSL https://openclaw.ai/install.sh | bash
After the installation script is executed, it automatically enters the Onboarding (initialization wizard) Process.
3. Initialization configuration and model selection
In the initialization wizard, it is recommended to select “QuickStart” Mode.
The system will ask to configure the default LLM (Large Language Model) provider. openClaw supports OpenAI, Anthropic and many other major vendors.
- Model recommendations: The demo uses Qwen (Tongyi Qianqian), which usually offers a certain amount of free calls (e.g. 2000 tokens per day) and is suitable for testing.
- authentication process: Since Codespaces runs in a cloud container, it is not possible to directly evoke a local browser. The terminal will generate an authentication URL, users need to manually copy the link to the local browser to open it, after completing the login authorization, OpenClaw can obtain the API Key.
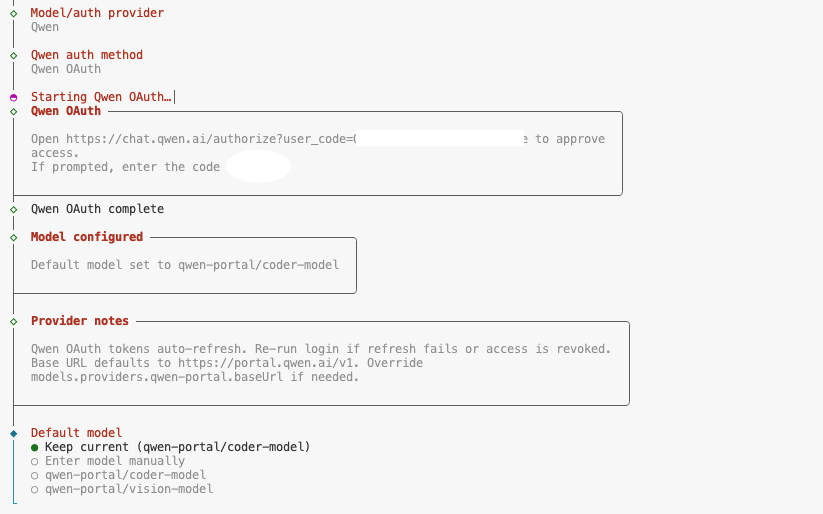
Just keep the defaults for subsequent configurations (enter all the way) and refer to the options in the following figure:
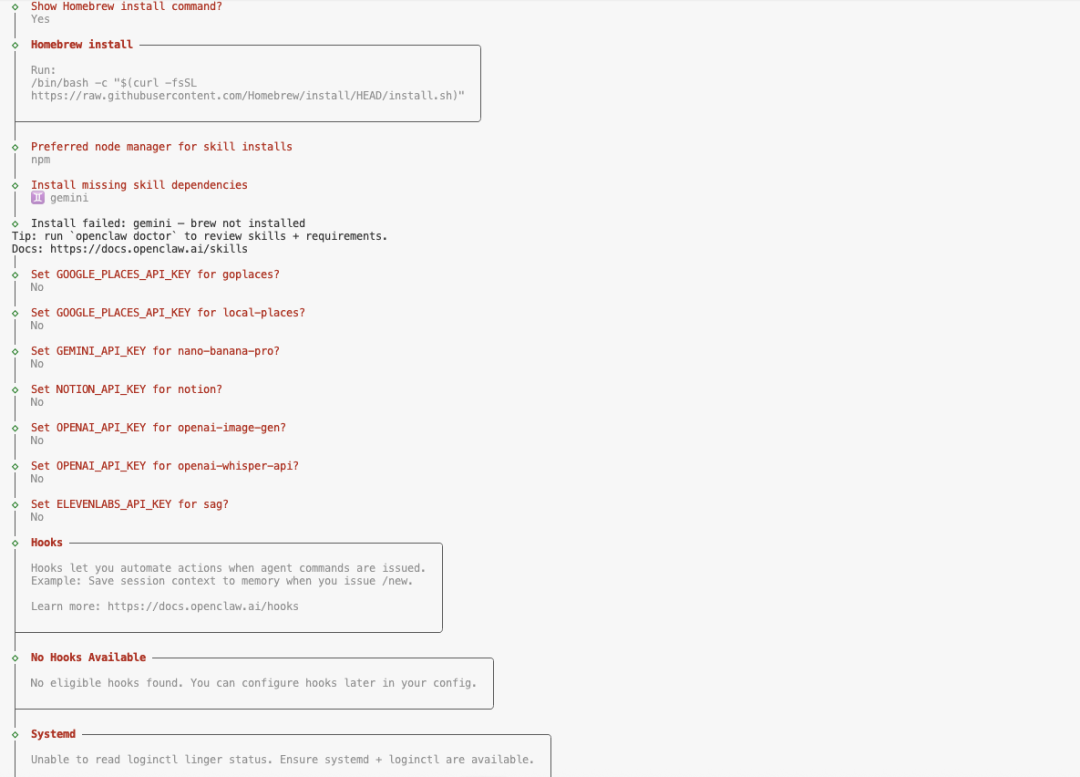
When the terminal displays Onboarding complete When pressing Ctrl + C Exit the current wizard process. At this point OpenClaw has been installed, but the service has not yet started.
4. Refinement of the Shell environment (optional)
For a better command line patching experience, it is recommended to install patching scripts based on the shell you are currently using:
# 如果使用 bash (Codespaces默认)
openclaw completion --install --shell bash
# 如果使用 zsh
openclaw completion --install --shell zsh
Phase 2: Launch Gateway and Service Guard
Codespaces itself does not have a background daemon management tool such as Systemd, so you need to start OpenClaw Gateway manually.
1. Launch Gateway
Gateway is the brain of OpenClaw. To avoid service interruptions caused by closing terminal tabs, it is recommended to use the nohup command runs it in the background and redirects the logs to the output.
# 后台启动命令,端口指定为18789
nohup openclaw gateway --port 18789 --verbose > ~/openclaw.log 2>&1 &
If you are not used to running in the background, you can also just execute the openclaw gateway --port 18789 --verbose, but keep that terminal window open at all times and execute subsequent commands in a new tab.
2. Validation of service status
Execute the following commands to confirm that the Gateway is functioning properly and the status of each module is healthy:
# 查看网关基础状态
openclaw gateway status
# 深度检查所有组件状态
openclaw status --deep
Phase III: Flying Book Open Platform Integration
The latest version of OpenClaw has a built-in flybook adapter, so there is no need to install third-party plugins. The next key is the configuration of the Flybook open platform.
1. Creating enterprise self-built applications
log in Flying Book Open PlatformClick “Create application” -> “Enterprise Build Your Own Application”。
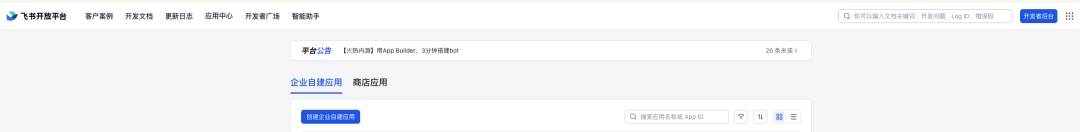
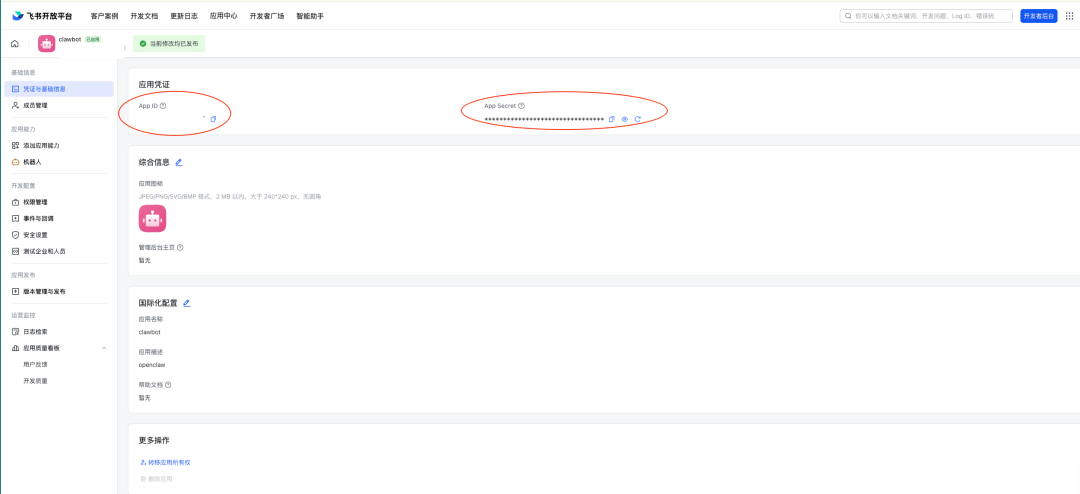
After successful creation, the “Vouchers and basic information” page to get the following key credentials:
- App ID (
cli_...beginning) - App Secret
Go back to the Codespaces terminal and configure OpenClaw's flybook channel parameters:
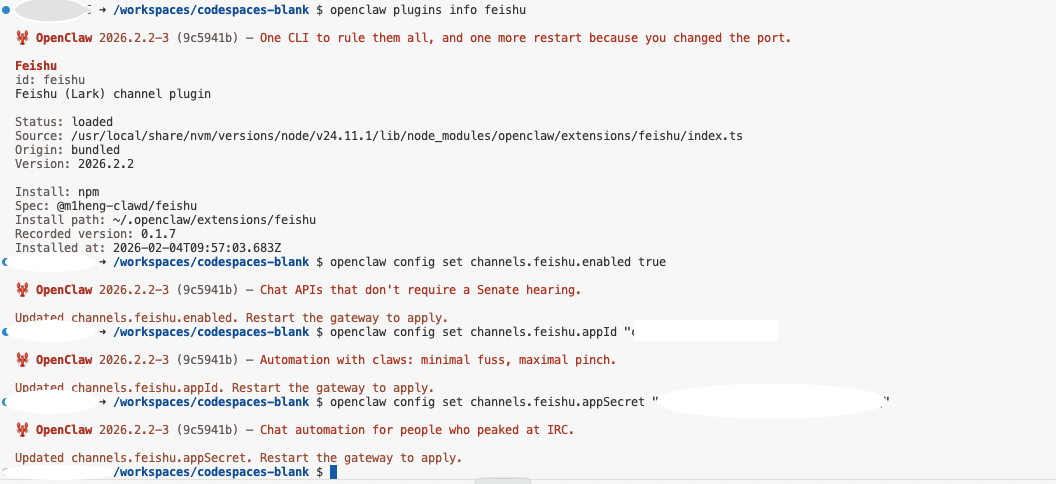
# 启用飞书通道
openclaw config set channels.feishu.enabled true
# 设置App ID (请替换为实际值)
openclaw config set channels.feishu.appId "cli_a1b2c3d4e5"
# 设置App Secret (请替换为实际值)
openclaw config set channels.feishu.appSecret "your_app_secret_here"
2. Permissions
On the Flying Book open platform of “Development Configuration” -> “Rights Management” In , search for and enable the following permissions to ensure that the bot can read and write messages:
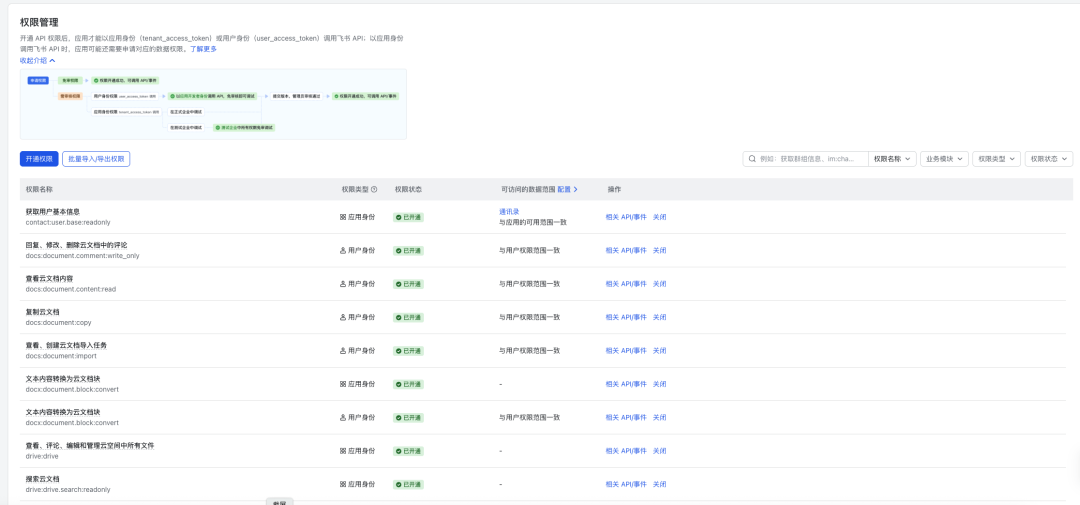
im:message(Getting and sending single chat, group messages)im:message.p2p_msg:readonly(Reads single chat messages sent to the bot by the user)im:message.group_at_msg:readonly(Reads messages from @bots in group chats)im:message:send_as_bot(Send message as application)im:resource(Getting and uploading images, file resources)
take note of: Once you have opened the privileges, you need to click on the top of the page “Create version” 并 “Release.”, the privilege change will not take effect.
3. Event Subscriptions
This is a critical step in achieving a public-free IP connection.
在 “Events and Callbacks” Page:
- Configuration method selection:Long connections (WebSocket). This way the Agent actively establishes a connection to the Flying Book server without having to penetrate a firewall.
- Add an event listener to subscribe to the following events:
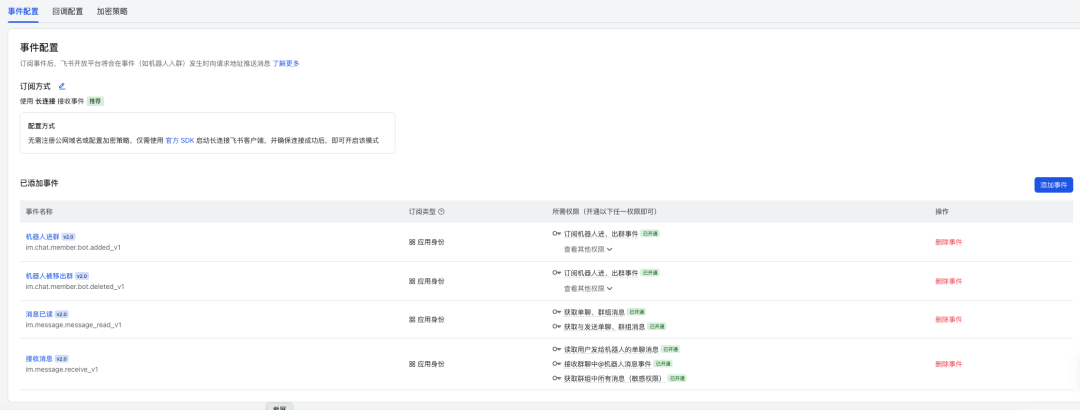
im.message.receive_v1(Receive Messages v1)im.message.message_read_v1(Message read notification)im.chat.member.bot.added_v1(Robot notification of group entry)im.chat.member.bot.deleted_v1(Bot removed from group notification)
Once the configuration is complete, go to the “Versioning and Distribution” page to release the latest version of the application.
Phase 4: Security Pairing and Field Testing
To prevent unauthorized users from abusing Agent resources, OpenClaw introduces the Pairing Mechanisms.
1. Triggering the pairing request
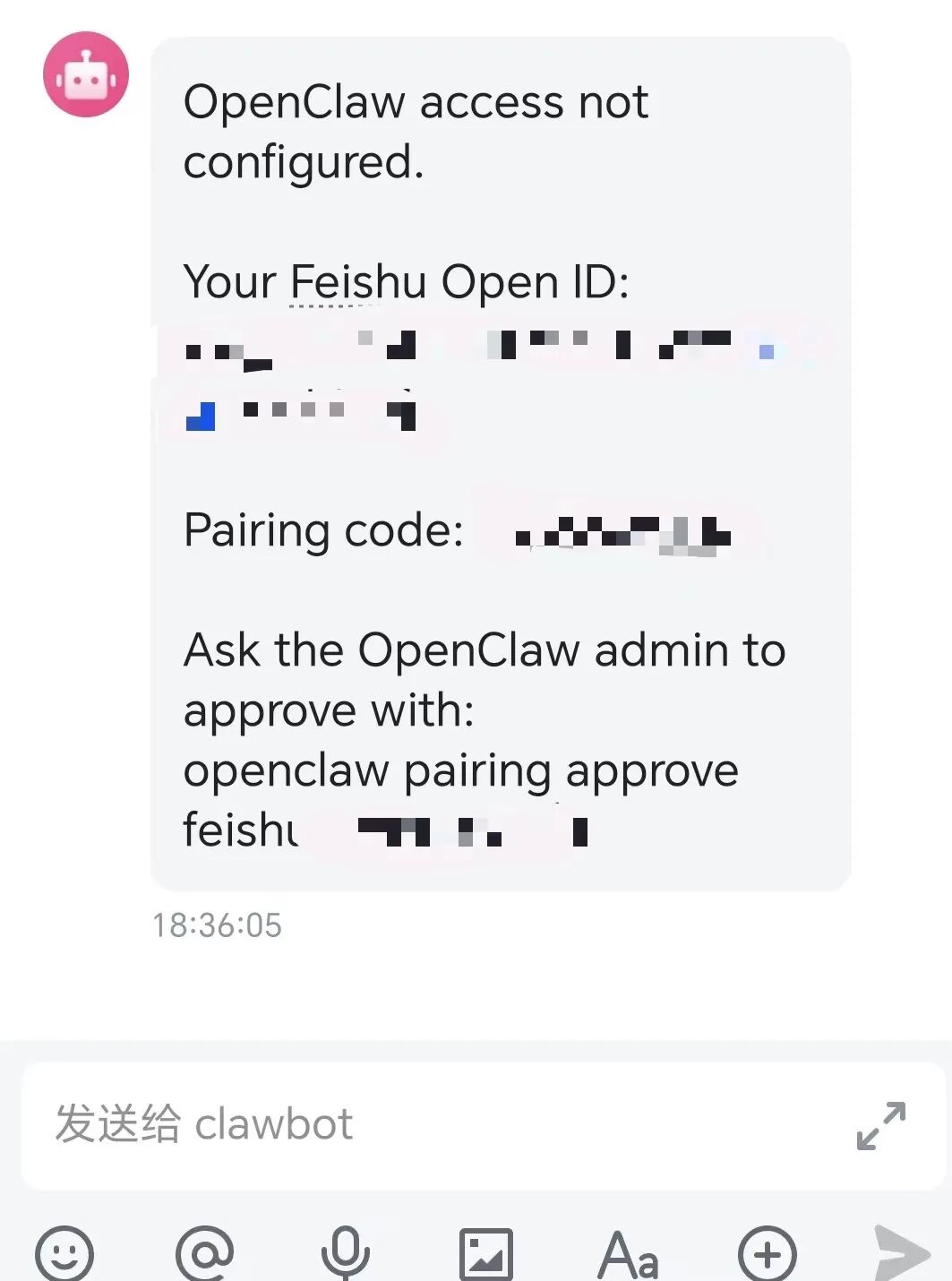
Find the bot you just created in the Flybook client and send it any message (e.g. “Hello”).
Instead of replying to the content, the bot will receive a system alert (or display it in the log) informing that it is currently in Pairing Mode and giving a pairing verification code.
2. Approval of matches
Back in the Codespaces terminal, use the following command to approve the connection request for this user (assuming an authentication code of ABCD1234):
openclaw pairing approve feishu ABCD1234
Once the approval is complete, OpenClaw will immediately process the message just sent and respond.
3. Setting up a whitelist (recommended for production environments)
Frequent pairing is not convenient if it needs to be used within the organization for a long period of time. This can be done by setting up a whitelisting policy to allow users with specific Open IDs to interact directly.
# 将策略改为白名单模式
openclaw config set channels.feishu.dmPolicy "allowlist"
# 添加允许的用户OpenID (JSON格式数组)
openclaw config set channels.feishu.allowFrom '["ou_xxxxxxxxxxxx"]'
Note: After modifying the configuration, it is recommended to restart the Gateway process to ensure that it takes effect.
summarize
Through the above steps, developers have successfully built a set of OpenClaw Agents with full interaction capabilities in the zero-cost environment of GitHub Codespaces, which takes advantage of the convenience of containerization technology and the reverse connectivity features of WebSocket to perfectly circumvent complex network penetration issues. Although Codespaces is suitable as a validation platform for MVP (Minimum Viable Product), after mastering this process, you can easily migrate it to any Docker-enabled long term runtime environment (e.g., EC2, QunHui NAS, or a local Raspberry Pi) to formally open the path of advancement for AI orchestrators.