Transforming a novel or screenplay into a split-screen script is a key part of creating film, television, animation and comics. This process requires creators to analyze the text in depth, sort out the plot, characters, scenes and dialogues, and then construct a series of continuous images through imagination. The traditional manual approach is not only time-consuming, but also a huge amount of work.
With the advancement of AI technology, a question naturally arises: can this onerous task be given to the AI? The answer is yes. By constructing rational workflows thatAI It is now possible to take a text chapter of up to 3,000 words and steadily convert it into a detailed split script containing 40 to 60 shots, while maintaining the integrity of the original plot and dialog.
In this paper, we will look at the direct use of AI Common problems encountered when performing split-screen conversions and provides a proven four-step workflow, concluding with an example tool showing how to automate this process.
Common Barriers to AI-Assisted Authoring
If the content of the novel is simply given directly to the AI and ask them to create a compositional mirror, often with unsatisfactory results. Creators typically face the following three core problems:
- Insufficient content reproduction
AIDuring the conversion process, sometimes unauthorized changes are made to the plot or dialogue. This is usually due to the fact that the formatting of the original text (especially web novels) is not standardized enough, resulting in theAIThere is a bias in understanding, resulting in content omissions or changes. - Too few shots
A complete chapter.AILess than 15, or even 10, shots may have been generated. This "gold rush" is a result of theAIFailure to adequately analyze the text for scene and action resulted in many visual details being overlooked. - Unexpected interruption of the generation process
Different Large Language Models (LLMs) have a limit on the total number of words in their input and output, i.e., a "context window". When dealing with long texts and requiring the generation of detailed transcripts, this limit can easily be exceeded, leading to an interruption of the generation task. This shows that it is extremely difficult to obtain the desired output from a single conversation.
Optimized AI split-screen authoring workflow
The key to solving the above problems is to change the relationship with the AI of interaction. Instead of issuing commands in one step, a step-by-step, guided strategy that allows the AI Step-by-step task completion. This approach is similar to the "Chain-of-Thought" in cue engineering, which significantly improves the quality of output by breaking a complex task into multiple simple subtasks.
A proven and efficient workflow consists of the following four steps:
1. Normative collation of content
This is the basis of the entire workflow. First, the raw text is given to the AI, ask it to reorganize the content and output a formatted and standardized version. For example, let AI Distinguish clearly [Scene Description]、[Characters Moving] 和 [Dialogue].. This step serves two purposes: one is to allow AI To "read" and understand the story in advance; and secondly, to provide a clearly structured textual basis for subsequent analysis and translation.
2. Estimated number of shots and structural distribution
在 AI After understanding the content, the next step is to make it macro-planning. Instructions AI Analyze the normalized text to estimate approximately how many shots will be needed to generate the composed script, and list the approximate distribution of these shots in key episodes or scenes. This step not only gives the creator an expectation of the final output, but also guides the AI Initial construction of the visual rhythm of the text.
3. Building core scenarios and character sheets
To ensure consistency of visual elements and to save token Consumption, the need to make AI Create detailed scene and character sheets. The benefits of this step are obvious: first, it generates specific scene and character descriptions, which provide a solid textual basis for possible subsequent AI paintings and ensure a consistent style. Second, in the final generation of the shots, only the names of the scenes and characters (e.g., "Scene 1", "Character A") need to be referenced, rather than repeating the details in each shot description, thus saving valuable contextual space and allowing for AI Generate more shots.
4. Integration of information generation into microscopy scripts
After all the above preparations, the last step is the logical integration of the output. To AI issue a final command asking it to combine the first three steps to generate the Normalized Script、Lens Predictive Distribution as well as Scene Character Sheetto create the full split script.
It has been proven that with this guided workflow, which includes at least three predecessor tasks, theAI The ability to generate far more detailed, accurate and complete split scripts than a single command.
Comparison of Workflow Effects: The Case of Kong Yijie
In order to visualize the difference between the two methods, we use Lu Xun's short story "Kong Yi Ji" for testing, and perform "one-step conversion" and "four-step workflow conversion" on the same large language model.
1. AI one-step direct conversion
Directly to the original text of "Kung Yee Ki AI After, the model ended up generating only 12 shots and lacked systematic scene and character descriptions, with many plot points and details being merged or ignored.

2. AI four-step workflow conversion
Through the aforementioned four-step workflow, theAI In the end, 59 subplots were generated. The script not only completely restored the storyline, but also added many shots used to portray characters, render scenes and realize transitions. In addition, the output also contains very detailed scene sheets and character sheets, which greatly facilitates the subsequent visual creation.


A more streamlined implementation: automated tools
Well-designed workflows can certainly dramatically improve AI performance. However, performing this four-step process manually, especially passing and organizing information across different dialog windows, is still time-consuming and labor-intensive, especially the manual conversion of the generated content into a tabular format.
To address this issue, tools that integrate such workflows have appeared on the market, such as 小镜故事板 (xjstoryboard)The system automates the entire process. Such tools automate the entire process so that the user simply enters the raw text and the system does all the analyzing and generating in one stop.
The process of its use is usually as follows:
- Paste text content
Paste chapters of a novel or screenplay in a specified area, usually supporting text processing of about 3000 words, enough to cover most single-chapter content.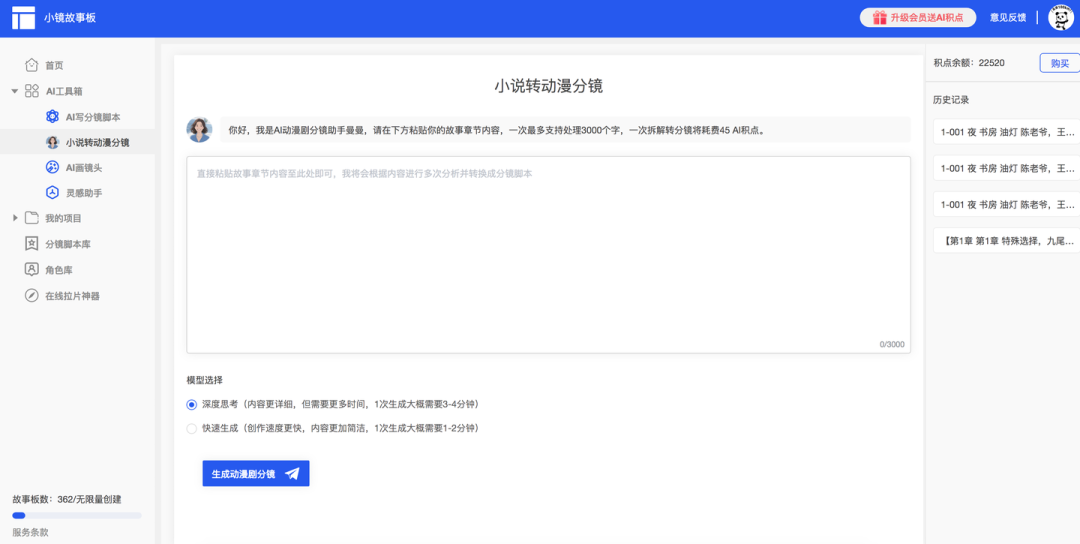
- AI automated workflow execution
The system's background will automatically execute the steps of content organization, shot estimation, and character scene construction, and output the generated content in panels.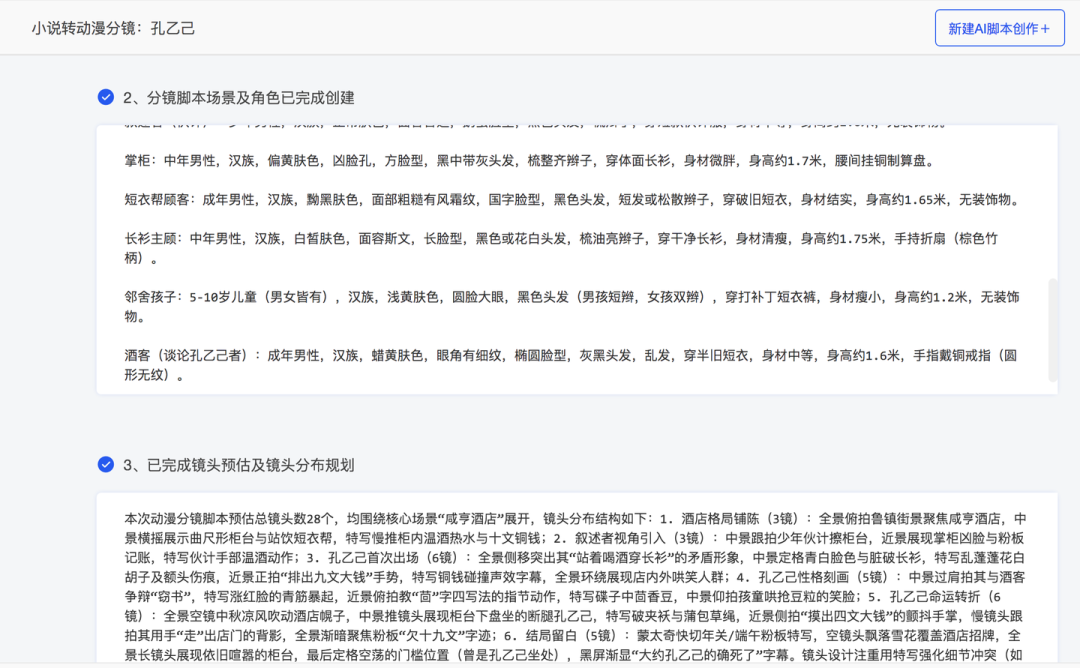
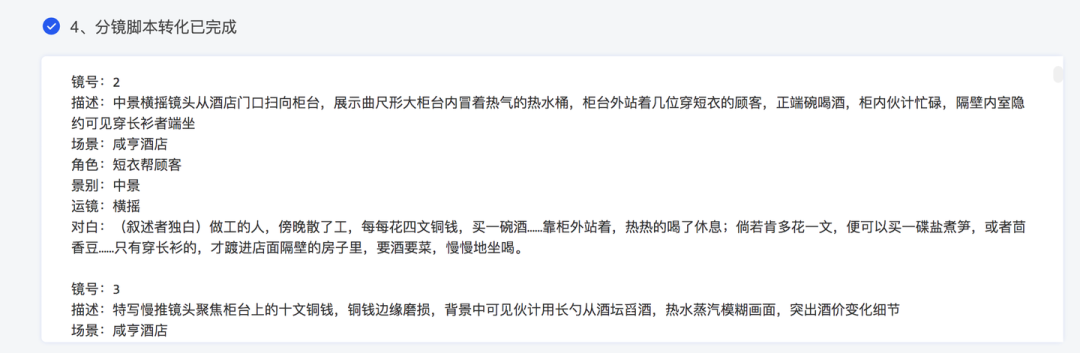
- Content categorization and table generation
AIAfter completing all text generation, the split scripts are automatically organized into structured tables.
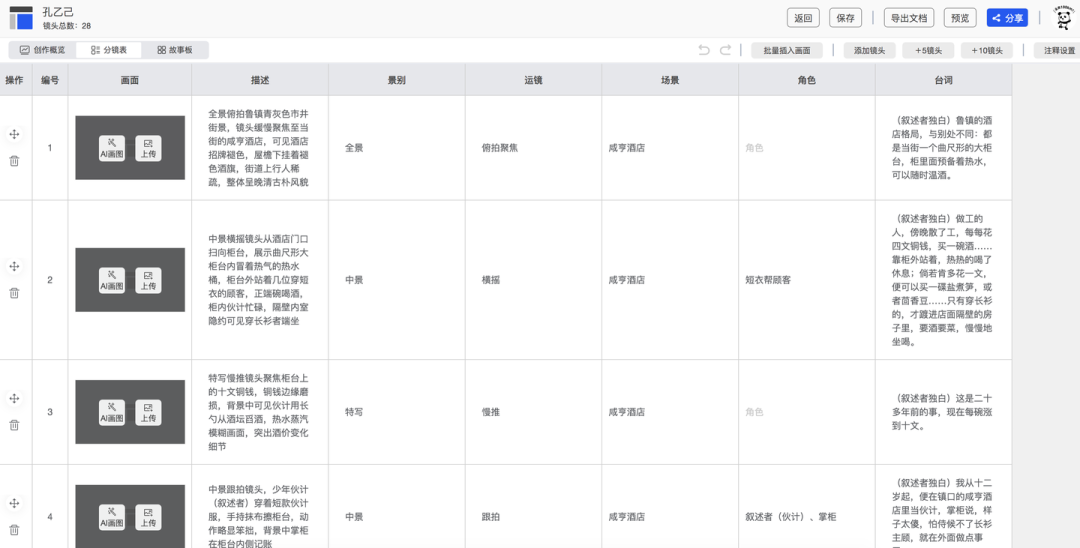
- Online editing and exporting
Users can make secondary edits to the generated content on the form page, drag and drop to adjust the order of shots, and ultimately export it as aExcel或PDFformat.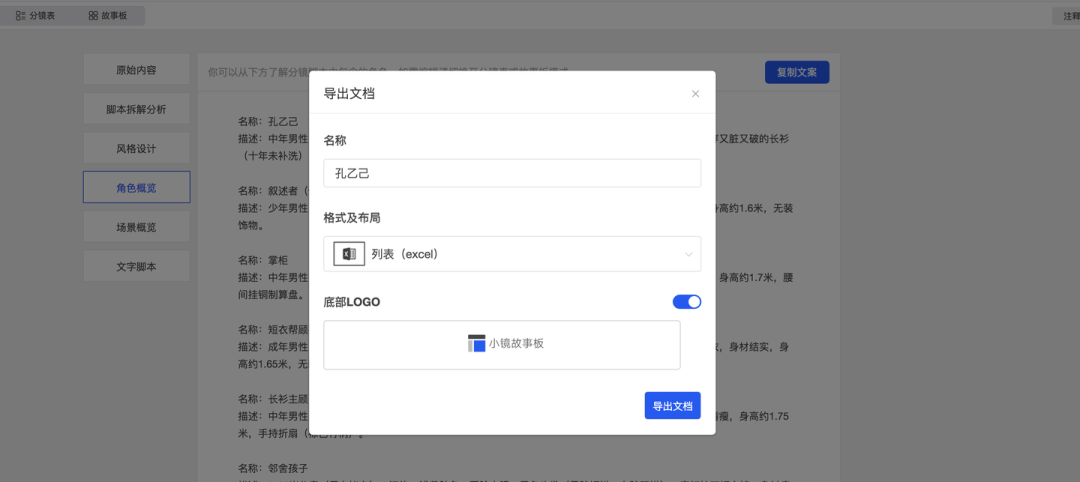
The core advantage of this type of automation tool is that the user only needs to provide the original text to get a complete, structured split-script, scene sheet and character sheet. Of course, a complete conversion usually takes several minutes due to the number of backend workflow steps.
Either manually in the GPT-4 或 Claude 3 Whether practicing this four-step workflow on a large model such as the AI From an unpredictable "black box" to a reliable and efficient creative assistant.