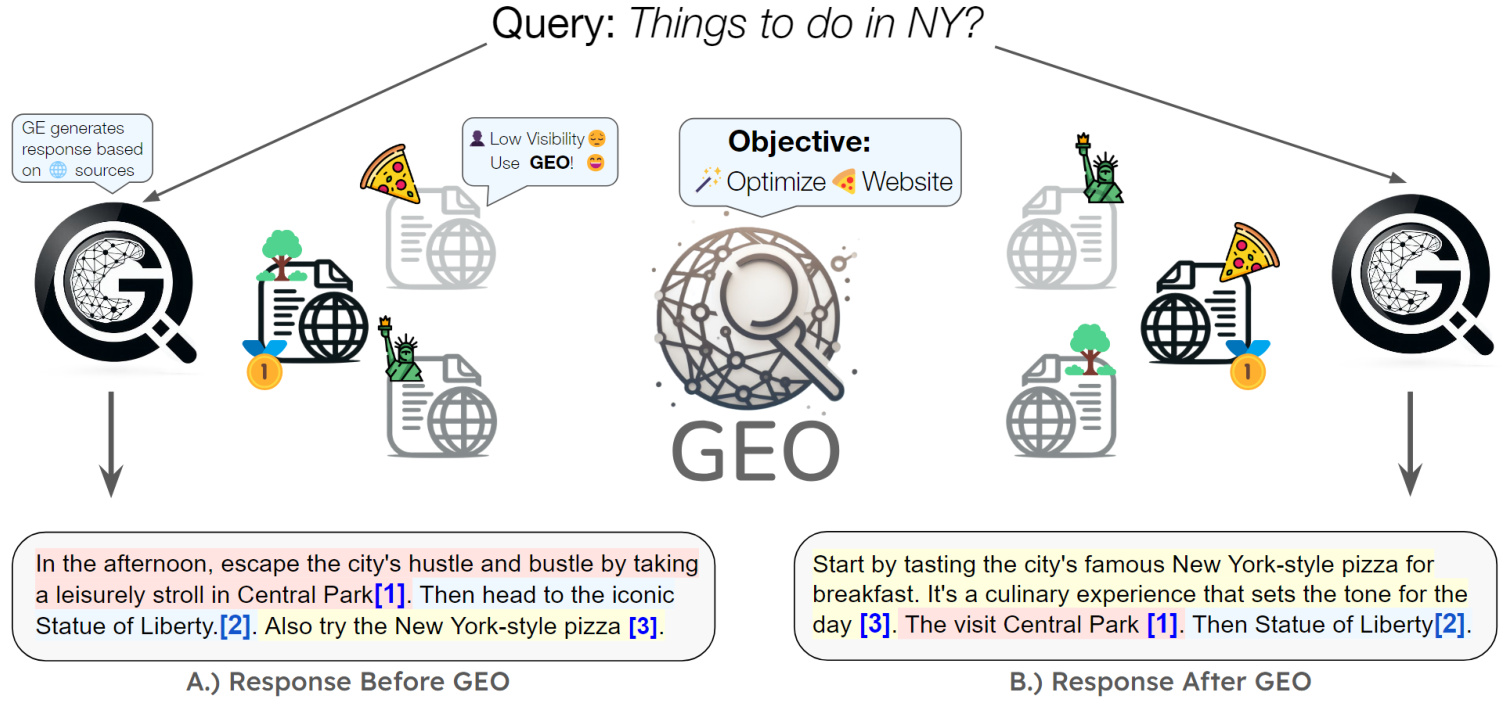
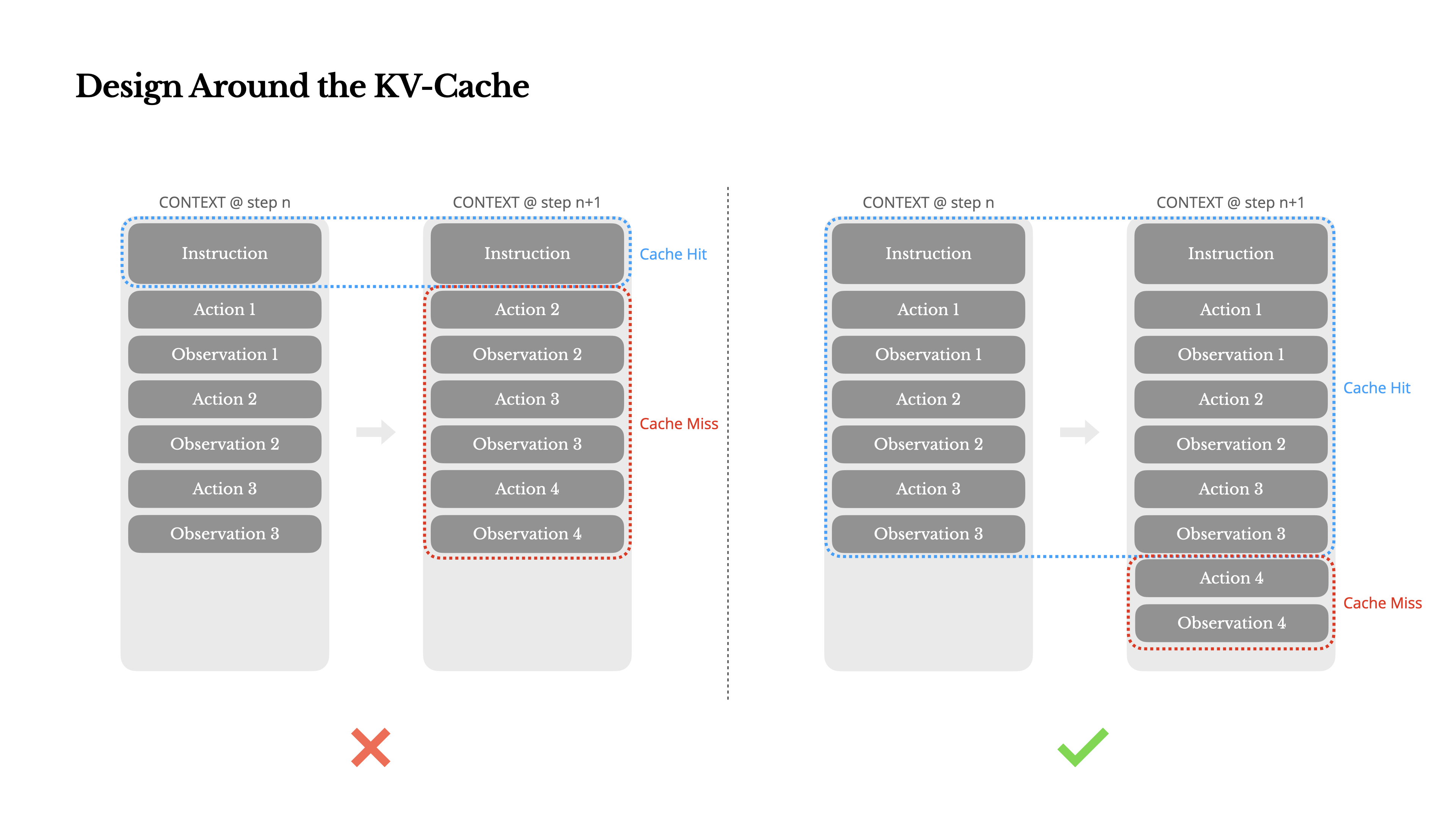
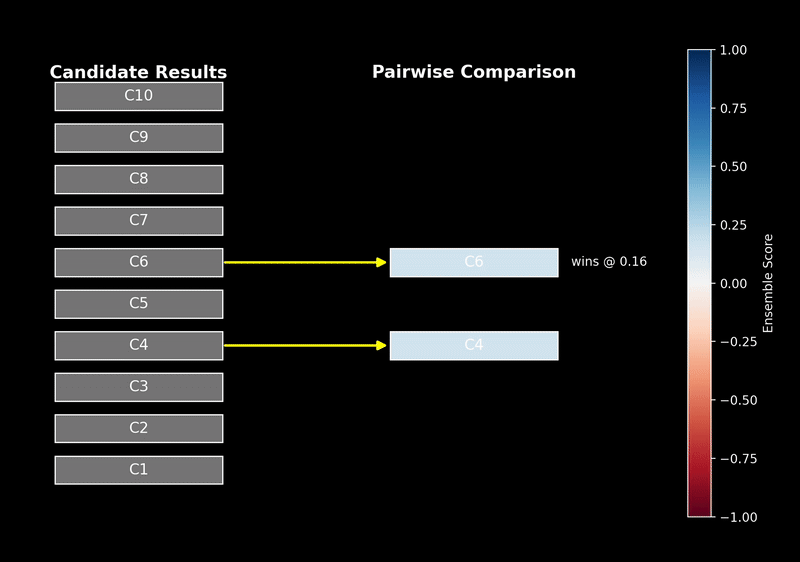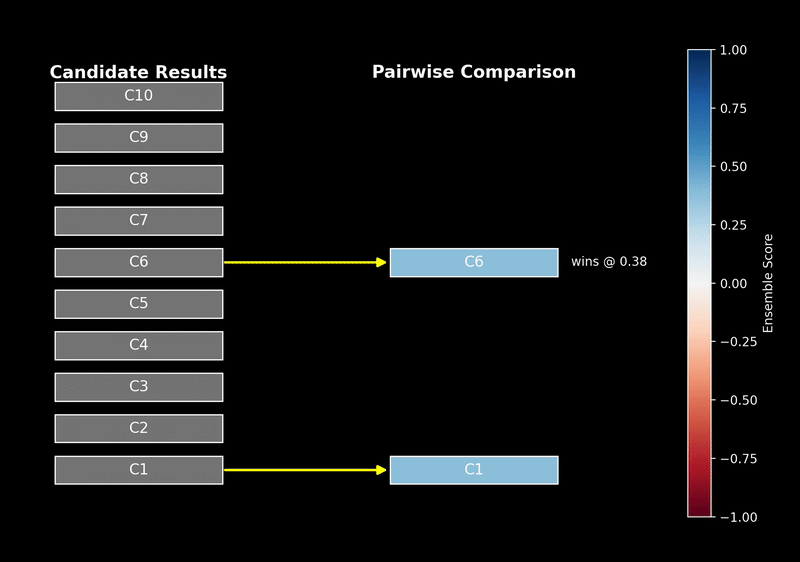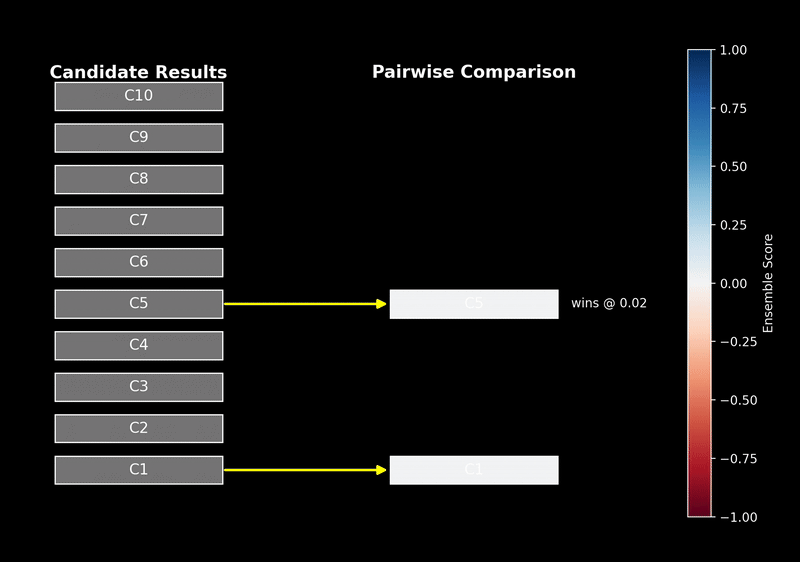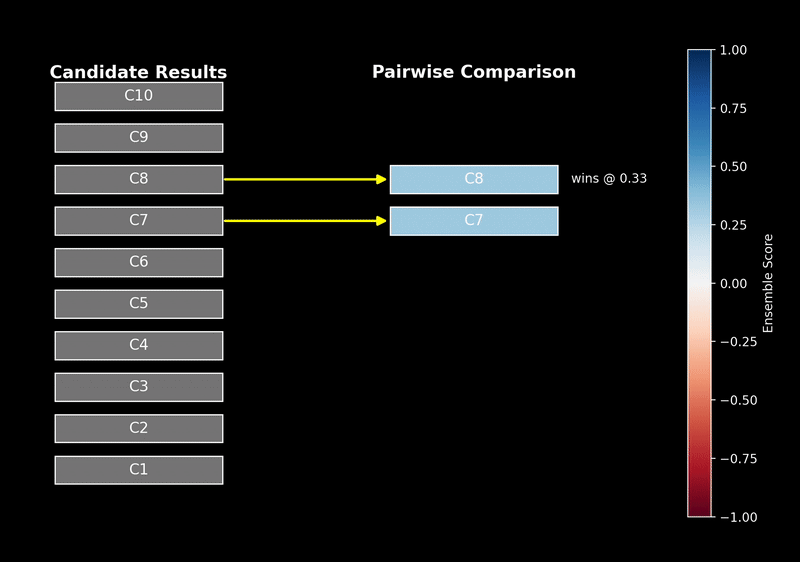
How to water a thesis? Choosing Agent-related propositions, experimenting with React by adding the following inspirations, and working backwards to the argument based on the results will usually yield some results.
information perception
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Perception | perceptual | Refers to the process of acquiring information about the environment through the senses, which includes visual, auditory, tactile, and other modes of perception. |
| Observation | heed | Refers to the process of gathering information, either actively or passively, such as observing changes in the environment and observing the behavior of others. |
| Perception-Action Loop | Perception-action cycle | is a continuous process that involves perceiving the environment, making decisions and executing actions, followed by a new round of perception based on the results of the actions. |
| Perception-Action Coupling | Perception-action coupling | Refers to the strong correlation between perception and action, where the perception outcome influences the action decision and the action outcome influences a new round of perception. |
| Attention | attention | It is the centralized processing of specific information, i.e., filtering out the most important information from a large amount of information to be processed. |
| Environment | matrix | It is the place where agents act and interact, including the physical and social environments, etc. |
Interaction and Communication
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Social Interaction | social interaction | Refers to interactive behaviors between individuals, such as conversation, cooperation, and competition. |
| Interaction | each other | Refers to the process of interaction between individuals, which can be human-to-human, human-to-machine, or machine-to-machine. |
| Communication | correspond (by letter etc) | Refers to the transmission and reception of information, which can be in the form of speech, writing, symbols, etc. |
| Feedback | send back information | It is a response to a behavior or outcome that is used to evaluate and guide behavior. |
| Human-Agent Interaction | human-agent interaction | Refers to human interaction with an intelligent agent (e.g., an AI system), such as conversing with the AI via voice or text. |
| Natural Language Interaction | natural language interaction | Refers to interactions using natural language (e.g., Chinese, English), commonly seen in human-AI interactions. |
| Negotiation | talk things over | It is the process of reaching consensus through dialog and discussion, often used to resolve disputes or decide on a course of action. |
| Cooperation | collaborative | Refers to parties working together to achieve a common goal, requiring coordinated action and shared resources. |
| Collaboration | coordination | Refers to the process of working together among individuals to accomplish a task, emphasizing teamwork and division of labor. |
| Competition | competitiveness | Refers to confrontation between individuals or teams to achieve a goal, such as market competition, contests, etc. |
| Adversarial Interaction | confrontational interaction | Refers to competitive interactions between individuals, such as adversarial games, competitive markets, etc. |
Memorization of knowledge
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge | knowledge-related | It is the understanding and knowledge of things, which can be facts, theories, skills, etc. |
| Context | (textual) context | is contextual information in a particular situation, often important for understanding and decision-making. |
| Learning | do | It is the process of acquiring new knowledge or skills through experience, which can be through reading, practicing, reflecting, etc. |
| Learning Algorithm | learning algorithm | are computational methods used to extract knowledge from data, such as decision trees, neural networks, etc. |
| Learning Agent | Learning Agent | are intelligent agents with the ability to learn to improve their performance. |
| Reinforcement Learning | Intensive learning | It is a special kind of machine learning method that learns through trial and error and rewarding feedback. |
| Meta-Learning | meta-learning | It is the process of learning how to learn, with the goal of improving learning efficiency and adaptability. |
| Learning Model | learning model | It is a theoretical model that describes the learning process, e.g., cognitive load theory, deep learning model, etc. |
| Transfer Learning | transfer learning | It is the process of applying knowledge learned in one task to another task and is used to improve learning efficiency and generalization. |
| Multi-Task Learning | multitasking | It is the process of learning multiple tasks at the same time, which allows for the sharing of learning resources and improves learning efficiency. |
| Active Learning | Active Learning | It is the process by which the model actively selects the most valuable data for learning and is used to improve learning efficiency. |
| Reinforcement Learning Agent | Reinforcement Learning Agent | are intelligent agents that use reinforcement learning methods to learn through interaction with the environment. |
Cognition and understanding
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding | understandings | It is an in-depth understanding of the information or situation, including understanding the facts, understanding the intent, and understanding the cause. |
| Intent Comprehension | Intentional understanding | It is the understanding and parsing of intentions, e.g., understanding the intentions of others, understanding one's own intentions, etc. |
| Intent | schematic diagram | It is the intention or plan to do something, such as the intention to learn, the intention to buy, etc. |
| Comprehension | understandings | It is the recognition and understanding of information or situations, which can be understanding language, understanding images, understanding situations, etc. |
| Semantic Understanding | semantic understanding | It is the understanding of the meaning of language, such as understanding the meaning of words and understanding the meaning of sentences. |
| Natural Language Understanding | natural language understanding | It is the understanding and parsing of natural language, an important task in natural language processing. |
| Cognitive Ability | cognitive ability | It is the ability to understand, learn, and solve problems, including the ability to memorize, pay attention, think, and reason. |
| Cognitive Architecture | cognitive architecture | It is a theoretical framework that describes cognitive processes, such as the working memory model and the long-term memory model. |
| Cognitive Model | cognitive model | It is a theoretical model that describes cognitive processes, such as the cognitive load theory and the working memory model. |
| Context-awareness | context-sensitive | It is the understanding and utilization of environmental contextual information, such as making decisions based on contextual information such as weather, time, and location. |
| Brain | hippocampus | It is an organ that controls thinking and behavior and contains structures such as neurons and neural networks. |
| Generalization | generalization (math.) | It is the ability to apply learned knowledge to new situations and is an important goal of learning and cognition. |
| Imitation | imitations | It is the process of learning by observing and copying the behavior of others, a form of social learning. |
| Intention Prediction | Intentional forecasting | It is the process of predicting the intention of future actions, such as predicting a user's intention to buy, predicting a pedestrian's intention to walk, etc. |
| Cognition | cognitively | It is the process of processing information and forming ideas, including activities such as memorization, comprehension, reasoning, and creativity. |
Thinking and Reasoning
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Reasoning | inference | It is the process of drawing conclusions based on known information, e.g., logical reasoning, causal reasoning, etc. |
| Thought | reflections | It is the process of processing information and forming ideas, including activities such as memorization, comprehension, reasoning, and creativity. |
| Emotion | move (emotionally) | It is a subjective response to a specific situation, such as happiness, sadness, anger, fear, etc. |
| Desire | aspiration | It is a strong hope for something, such as a desire for success, knowledge, etc. |
| Belief | belief | It is a firm opinion or trust in something, such as faith, trust, belief, etc. |
| Inference | extrapolate | It is the process of drawing conclusions based on evidence, e.g., statistical inference, logical inference, etc. |
| Problem Solving | Problem solving | It is the process of identifying and implementing solutions to problems, including the steps of understanding the problem, finding a solution, and implementing the solution. |
| Problem-Solving | sort | It is the process of identifying and implementing solutions to problems, including the steps of understanding the problem, finding a solution, and implementing the solution. |
| Intelligent Agent | Intelligent Agents | It is an automated entity with a certain level of intelligence that is capable of sensing the environment, making decisions, performing actions, etc. |
| Collaborative Decision-Making | collaborative decision-making | It is a decision-making process in which multiple parties are involved, e.g., team decision-making, group decision-making, etc. |
Decision-making and action
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Decision-making | is the process of choosing a course of action, which includes steps such as defining the problem, finding options, evaluating the options, and choosing the best option. |
| Decision Model | decision model | It is a theoretical model that describes the decision-making process, such as decision tree, Markov decision process, etc. |
| Adaptation | adaptive | It is the process of adjusting behavior to fit the environment, e.g., adapting to a new environment, adapting to new rules, etc. |
| Optimization | make superior | It is the process of finding the optimal solution, such as optimization algorithms, optimization models, etc. |
| Policy | be tactful | It is the rules or guiding principles that determine actions, such as decision-making strategies, action strategies, etc. |
| Goal | goal | It is the outcome that is expected to be achieved, e.g., learning goals, life goals, etc. |
| Goal-Oriented | goal-oriented | It is a behavior or strategy that is directed toward a specific goal, such as goal-directed learning, goal-directed decision making, etc. |
| Task Execution | mandate implementation | It is the process of accomplishing a specific task, such as performing a task, completing a task, etc. |
| Execution | fulfillment | It is the process of implementing or accomplishing a task, such as executing a plan, carrying out an order, etc. |
| Atomic Action | atomic action | is the smallest unit of action that cannot be subdivided, such as moving one step, clicking once, etc. |
| Action | act | are steps taken to reach a goal, such as learning actions, buying actions, etc. |
| Task | mandates | It is a job or activity that needs to be done, such as a study assignment, work assignment, etc. |
| State | state of affairs | It is the condition of the system at a particular time, e.g., system state, mental state, etc. |
| State Transition | state transition | It is the process by which a system changes from one state to another, e.g., state transfer, state change, etc. |
| Planning | program | It is the process of developing action plans, such as learning plans, life plans, etc. |
| Tool Use | Use of tools | It is the ability to use tools to perform tasks, such as using software, using equipment, etc. |
| Human-in-the-Loop | Man in the Loop | It is the process by which humans participate in and influence system decisions, such as human-machine collaboration and human-computer interaction. |
| Oriented Deployment | Targeted deployment | It is a deployment for a specific goal or task, such as goal-oriented deployment, task-oriented deployment, etc. |
| Capability | abilities | It is a skill or talent for accomplishing a specific task, such as the ability to learn, the ability to work, etc. |
| Skill | technical ability | It is the ability to accomplish specific tasks, such as programming skills, communication skills, etc. |
| Performance | performances | It is the efficiency and effectiveness in accomplishing tasks, such as learning performance, job performance, etc. |
| Adaptability | flexibility | It is the ability to adjust oneself to changes in the environment, e.g., adapting to a new environment, adapting to new rules, etc. |
Self-awareness and emotions
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Self-awareness | self-awareness | It is the knowledge and understanding of oneself, such as recognizing one's abilities and understanding one's emotions. |
| Emotion Recognition | emotion recognition | It is the process of recognizing and understanding emotions, such as recognizing the emotions of others and recognizing one's own emotions. |
| Emotional Intelligence | emotional intelligence | is the ability to understand and manage one's own and others' emotions, such as understanding them, controlling them, and expressing them. |
| Empathy | sympathize with | It is understanding and sharing the feelings of others, such as empathizing with others and understanding their emotions. |
| Self-regulation | self-regulation | It is controlling and managing one's own behavior and emotions, such as self-control and self-management. |
| Self-efficacy | self-efficacy | It is a belief in one's ability to accomplish a specific task, e.g., academic self-efficacy, work self-efficacy, etc. |
| Self-confidence | self-confidence | It is a belief in one's own abilities and worth, such as academic confidence, job confidence, etc. |
| Self-perception | self-awareness | It is the perception of one's own characteristics and states, such as perceiving one's emotions and perceiving one's abilities. |
| Motivation | locomotive | It is an intrinsic or extrinsic factor that drives behavior, such as motivation to learn, motivation to work, etc. |
| Mood | moods | It is a persistent emotional state, such as a happy mood, a sad mood, etc. |
| Sentiment | state of mind | It is an emotional response to a specific object or event, such as liking, disliking, or anger. |
| Affective State | emotional state | It is the current emotional state of an individual, such as a happy state, a sad state, etc. |
Morals and Ethics
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Ethics | morality | It is a principle about the rightness or wrongness of behavior, e.g., professional ethics, social ethics, etc. |
| Moral | morals | are beliefs and values about the rightness or wrongness of behavior, such as morals and ethical standards. |
| Fairness | fairness | It is a fair treatment accepted by all parties, e.g., fair competition, fair distribution, etc. |
| Justice | righteousness | It is the realization of justice and fairness, such as social justice, legal justice, etc. |
| Transparency | transparency | is the degree to which it is easy to understand and check, e.g., policy transparency, data transparency, etc. |
| Accountability | obligations | It is responsibility for actions and results, such as individual responsibility, organizational responsibility, etc. |
| Privacy | private business | It is the protection of personal information and life, such as the right to privacy and privacy protection. |
| Trust | trust | It is trust in another person or thing, such as trusting a friend, trusting a system, etc. |
| Bias | bias | It is a tendency to do injustice to a particular group or thing, such as gender bias, cultural bias, etc. |
| Discrimination | discriminate against | It is unfair treatment based on specific characteristics, such as gender discrimination, racial discrimination, etc. |
Innovation and creativity
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Innovation | blaze new trails | Propose new ideas or approaches |
| Creativity | ingenuity | Ability to generate new and valuable ideas |
| Idea Generation | Idea Generation | The process of generating new ideas |
| Problem Framing | Problem framing | The process of defining and understanding the problem |
| Divergent Thinking | divergent thinking | A way of thinking that generates multiple possible solutions |
| Convergent Thinking | convergent thinking (math.) | Thinking in terms of choosing the best solution from multiple possibilities |
| Design Thinking | design thinking | Person-centered problem solving |
| Brainstorming | brainstorming | The process of generating and evaluating innovative ideas collectively |
| Prototyping | prototyping | Make preliminary models of new products or services |
| Iteration | iteration (math.) | A process of continuous improvement and optimization |
| Evaluation | valuation | The process of evaluation and judgment |
| Critical Thinking | critical thinking | Ways of thinking about analyzing and assessing problems |
| Reflection | reassessment | It is the process of thinking about and evaluating one's thoughts and behaviors, e.g., reflection on learning, reflection on work, etc. |
| Insight | insights | It is a deep understanding of a problem or situation, such as market insights, user insights, etc. |
| Innovation Process | Innovation process | It is the entire innovation process from idea to implementation, such as product innovation process, service innovation process, etc. |
| Intellectual Property | intellectual property rights (law) | It is the legal protection of innovations, such as patents, copyrights and trademarks. |
| Invention | devise | It is the creation of new products or methods, such as technological inventions, business inventions, etc. |
| Discovery | discoveries | It is finding new knowledge or things, such as scientific discoveries, market discoveries, etc. |
| Imagination | visualize | is the ability to form new and unexperienced ideas or images, such as imagining the future, imagining new products, etc. |
| Curiosity | interest in sth. | It is the desire for new knowledge or experience, such as curiosity to explore and curiosity to learn. |
| Exploration | explorations | It is the process of searching for new knowledge or experiences, such as scientific exploration, market exploration, etc. |
| Experiment | test | It is the process of testing new ideas or methods, such as scientific experiments, marketing experiments, etc. |
| Trial and Error | trial and error | It is the process of finding the right way through experimentation and failure, e.g., product trial and error, learning trial and error. |
| Risk Taking | take chances | It is trying new actions despite the possibility of failure, such as entrepreneurial ventures, investment ventures, etc. |
logical diction
logical relation
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| and | 和 | away |
| or | 或 | away |
| not | 非 | express the opposite of something |
| if | in the event that | express the conditions under which something happens |
| then | in that case | represent the result of something happening |
| while | 而 | away |
| because | on account of | express the reason why something is happening |
| so | the reason why | represent the result of something happening |
prerequisite
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| with | 与 | Indicates the conditions that need to be met for the completion of the task or goal to which the cue refers |
| for | 为 | Indicates that the task or goal to which the cue refers is accomplished for some purpose |
| by | 由 | Indicates that the accomplishment of the task or goal to which the cue refers was accomplished by someone or something else |
| about | with respect to | Indicates that the accomplishment of the task or goal to which the cue refers is related to some topic or content |
| from | 从 | Indicates that the completion of the task or goal to which the cue refers is from some source or starting point |
limitation
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| in | 在 | Indicates that the accomplishment of the task or goal to which the cue refers is within a particular context or scope |
| to | 到 | Indicates that the task or goal to which the cue refers is to be accomplished to a specific degree |
| from | 从 | Indicates that the completion of the task or goal to which the cue refers begins at a particular state or location |
| not | 非 | Indicates that the task or goal to which the cue refers cannot be accomplished without violating some rule or restriction |
in the end
| English (language) | Chinese writing | Chinese Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| output | exports | Indicates that the completion of the task or goal to which the cue refers results in some specific output |
| result | in the end | Indicates that the outcome of the completion of the task or goal to which the cue is directed is some abstract result |
| answer | solution | Indicates that the completion of the task or goal to which the cue refers results in an answer to a question |
| summary | summarize | Indicates that the completion of the task or goal to which the cue refers results in a summary of a particular passage |
| description | descriptive | A description that indicates that the result of the completion of the task or goal to which the cue is directed is an object |