Async is an open source developer tool that deeply integrates the three components of AI coding, task management and code review into one workflow. The tool aims to solve the development challenges of mature codebases by automating the entire process of merging from GitHub issues (Issue) to pull requests (Pull Request) to improve development efficiency. It starts by using AI to analyze coding tasks and ask questions to clarify requirements, then executes code changes in an isolated environment in the cloud and breaks down large tasks into multiple subtasks that are easy to review. In this way, Async reduces the frequency of developers switching between tools, forces planning before coding, and streamlines the process of task tracking and code review.
Function List
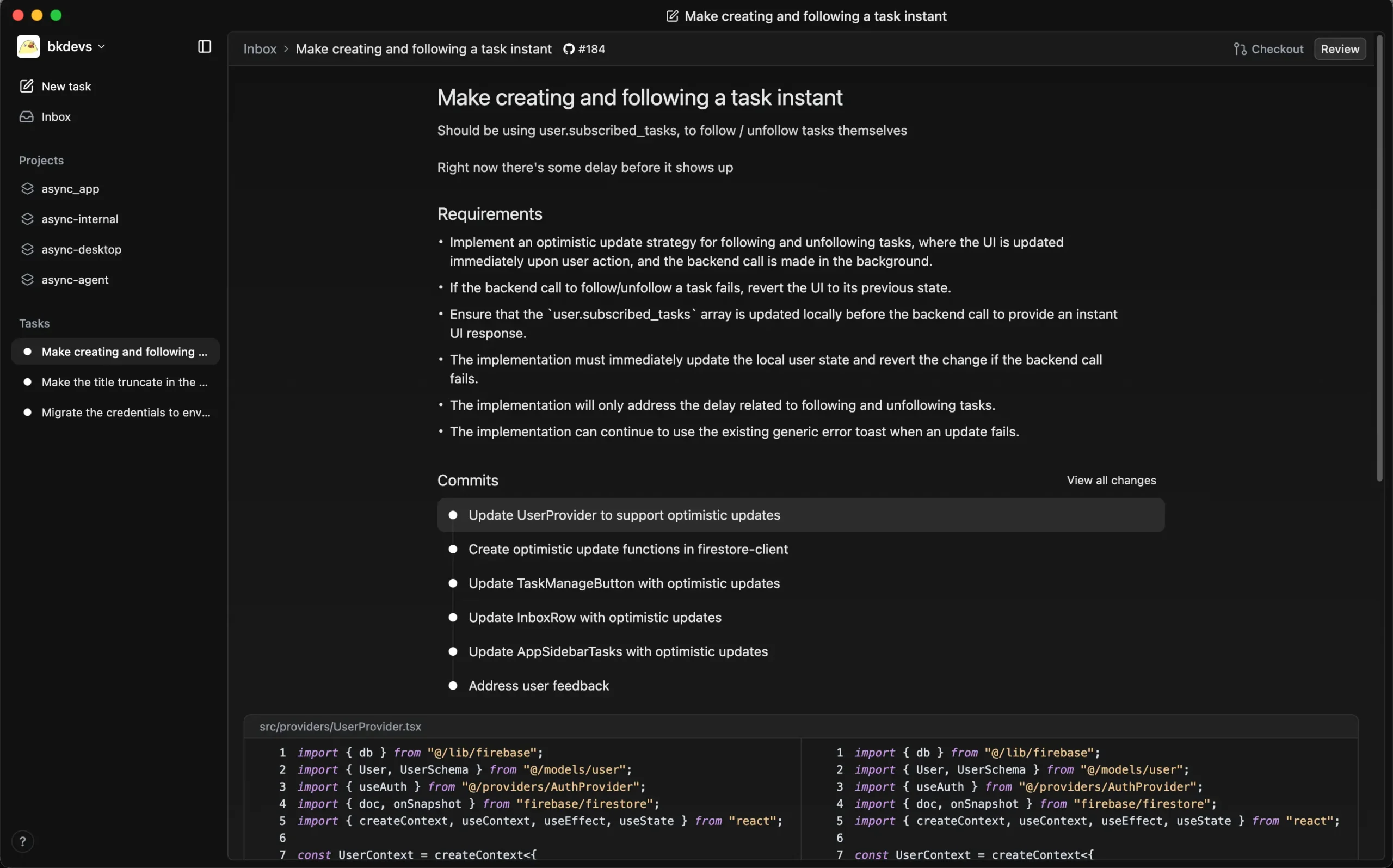
- Automated mission research: Before you start coding, Async automatically analyzes the code base and asks clarifying questions about the task requirements to make sure it's going in the right direction.
- Isolated execution in the cloud: Code modification and execution takes place in an isolated environment in the cloud without affecting the developer's local development environment, and the developer can handle other work in the meantime.
- Stacked variance review: It breaks down a large task into multiple independent subtasks and commits, generating stacked diffs that make the code review process clearer and more efficient.
- End-to-end workflow: Async handles the complete development process from the creation of a GitHub issue to the final merging of the code, all without the user ever leaving the app.
- Simplify task tracking: The tool automatically imports pending issues from GitHub repositories as tasks without the need to use additional project management tools.
- Built-in code review: Code submissions can be commented on and iterated on directly within the Async app, and can be merged directly after review.
Using Help
Async, as a complex application that integrates front and back ends, requires a series of environment configurations for its installation and use. The following section details how to deploy and run Async in your local environment.
environmental preparation
Before you start, make sure you have the Python Environment Manager tool installed on your system. The project recommends using theuv, a fast Python package installer and parser.
Step 1: Getting the code and setting up the virtual environment
- First, clone the project's code repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/bkdevs/async-server.git cd async-server - utilization
uvCreate a new virtual environment. This will create a new virtual environment in the home directory called.venvfolder to isolate project dependencies.uv venv .venv - Activate the virtual environment you just created. Under macOS or Linux, run it:
source .venv/bin/activate ``` 激活后,你的命令行提示符前端会显示`(.venv)`字样。
Step 2: Install project dependencies
- After activating the virtual environment, use the
uv synccommand to install thepyproject.tomlAll dependencies defined in the file.uv sync - Next, install the pre-commit hooks for code formatting and static checking.
pre-commit installThis ensures that when you submit your code, it automatically follows the specifications set by the project.
Step 3: Configuration file
- environment variable file:
In the root directory of your project, you need to create a.envfile. This file is used to store sensitive API keys and configuration information. You can refer to the project's.env.localfile to see what variables need to be configured.cp .env.local .envThen, edit the
.envfile, fill in your own configuration information, such as the database address, GitHub key, and API keys for Anthropic, OpenAI, Google, and other AI models. - Firebase Configuration Files:
The project uses Firebase Firestore as the database. You need to download the JSON key file for the service account from your Firebase project console and name itasync-firebase.json, and then placed in the root directory of the project. - Google Cloud Certification:
Since Async utilizes Google Cloud Run to perform cloud tasks, you need to authenticate locally for Google Cloud. Run the following command and it will open a browser to guide you through the login authorization:gcloud auth application-default login
Step 4: Run locally
- Start the back-end service:
After completing all the above configurations, you can start the back-end FastAPI service. Start it with the following command and the service will run8000port, and--reloadparameter will cause the service to restart automatically after a code change.uvicorn src.server:app --reload --port 8000 - Code checking and formatting:
If you want to format and style check your code manually, you can run the following command:# 格式化代码 uv run ruff format . # 检查代码并自动修复问题 uv run ruff check . --fix
Step 5: Run the test
To make sure everything functions properly, you can run the unit tests that come with the project:
python -m pytest
Workflow Introduction
When you run Async successfully locally, it works as follows:
- Authorization and task import: Authorize Async to access your code repository through the GitHub App, and it will automatically import unresolved Issues in the repository as tasks.
- research phase: When a new task is created, Google Cloud Run starts a "research" task that clones your codebase, analyzes the code, and generates questions about ambiguous requirements.
- Implementation phase: After you have confirmed or answered the question, another separate cloud-based task will start executing the code changes. It will use the Claude Code model to create a new functional branch, break the task into multiple subtasks and submit them one by one as commits, and finally create a pull request (PR) automatically.
- Review phase: You can review this PR in Async's interface, whose stacked diffs view lets you examine each subtask's changes individually. You can comment directly, and if changes are needed, the system automatically creates a new subtask; if the review passes, the code is merged.
application scenario
- Accelerate feature development for complex codebases
For teams with large and complex code bases, introducing new features or fixing deep vulnerabilities often requires a lot of upfront research and contextual understanding. async can help seasoned developers quickly locate modifications and spend less time manually figuring things out by automatically analyzing the codebase and clarifying the task requirements through its AI research capabilities. - Optimize the code review process
In fast-paced development teams, large Pull Requests often slow down reviews. async improves review efficiency and quality by breaking down a large task into multiple, logical subtasks (stacked diffs), allowing reviewers to break it down one by one and more easily understand the intent of each code change. - Reduce context switching during development
Developers often need to switch back and forth between IDEs, project management tools (such as Jira or Linear), code hosting platforms (GitHub), and communication tools. async integrates these processes into a unified platform, so that everything from task assignment, coding execution, and code review can be done in one place, dramatically reducing the mental burden of tool switching.
QA
- What is the main problem that the Async tool solves?
Async focuses on solving the efficiency problems encountered when developing in mature and complex codebases. It automates the entire process from issue creation to code merge by integrating AI coding, task management, and code review, and is designed to reduce developer context switching, enforce upfront planning, and streamline the code review process. - How does Async execute code in the cloud?
Async uses Google Cloud Run to run standalone, containerized tasks. When code changes need to be executed, it starts a cloud job that clones the code repository into an isolated environment, installs all dependencies, and then writes and commits the code using an AI model such as Claude Code, which automatically initiates a pull request upon completion. The whole process does not affect the developer's local environment. - Does the program support self-hosting (self-host)?
Yes, being an open source project, Async provides detailed guides for deployment both locally and in the cloud. Users need to configure Cloud Run and Firebase under their Google Cloud Platform account and provide the relevant API keys to deploy and run the entire service on their own. - Is this tool suitable for novice developers or new projects?
According to its documentation, Async is "built for experienced developers who know their code base in depth". It is most valuable when working on large projects with complex histories and structures. For brand new projects or junior developers, its complex automated processes may not be necessary.

































