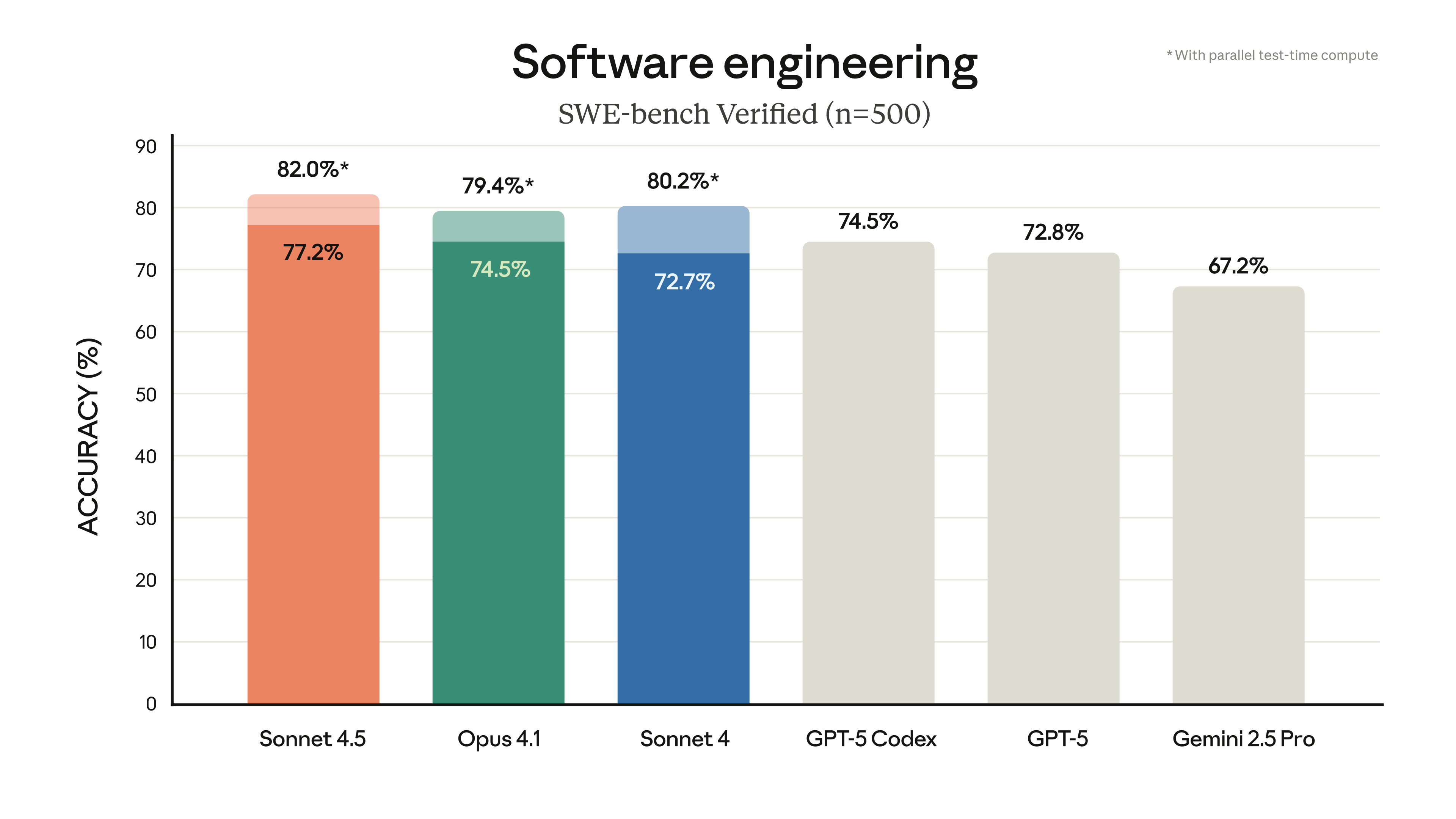
pain point analysis
Traditional document retrieval returns the full document content, resulting in an inefficient occupation of the LLM context window.DiffMem solves this problem with a three-level optimization strategy:
Core Optimization Program
- Current State Focus: index only the latest version of Markdown files by default to avoid historical versions from taking up the token
- Depth grading control::
depth="basic": return core nodes of the entity relationship graph (~50-100 tokens)depth="wide": Contains 2nd degree associated entities (~200-300 tokens)depth="deep": Trigger semantic search to return full content
- BM25 Dynamic Cropping: automatically extracts the 3 most relevant paragraphs for long documents
Example of implementation
# 获取精简上下文
context = memory.get_context("用户查询", depth="basic")
# 与LLM交互时组合提示词
prompt = f"基于以下上下文:{context}n回答:{query}"Effect Comparison
Tests showed compared to traditional methods:
- Base query saves 68% token consumption
- Response Latency Reduction 40%
- 22% increase in answer accuracy (due to noise reduction)
This answer comes from the articleDiffMem: a Git-based versioned memory repository for AI intelligencesThe