Core Architecture and Functional Positioning of MIRIX
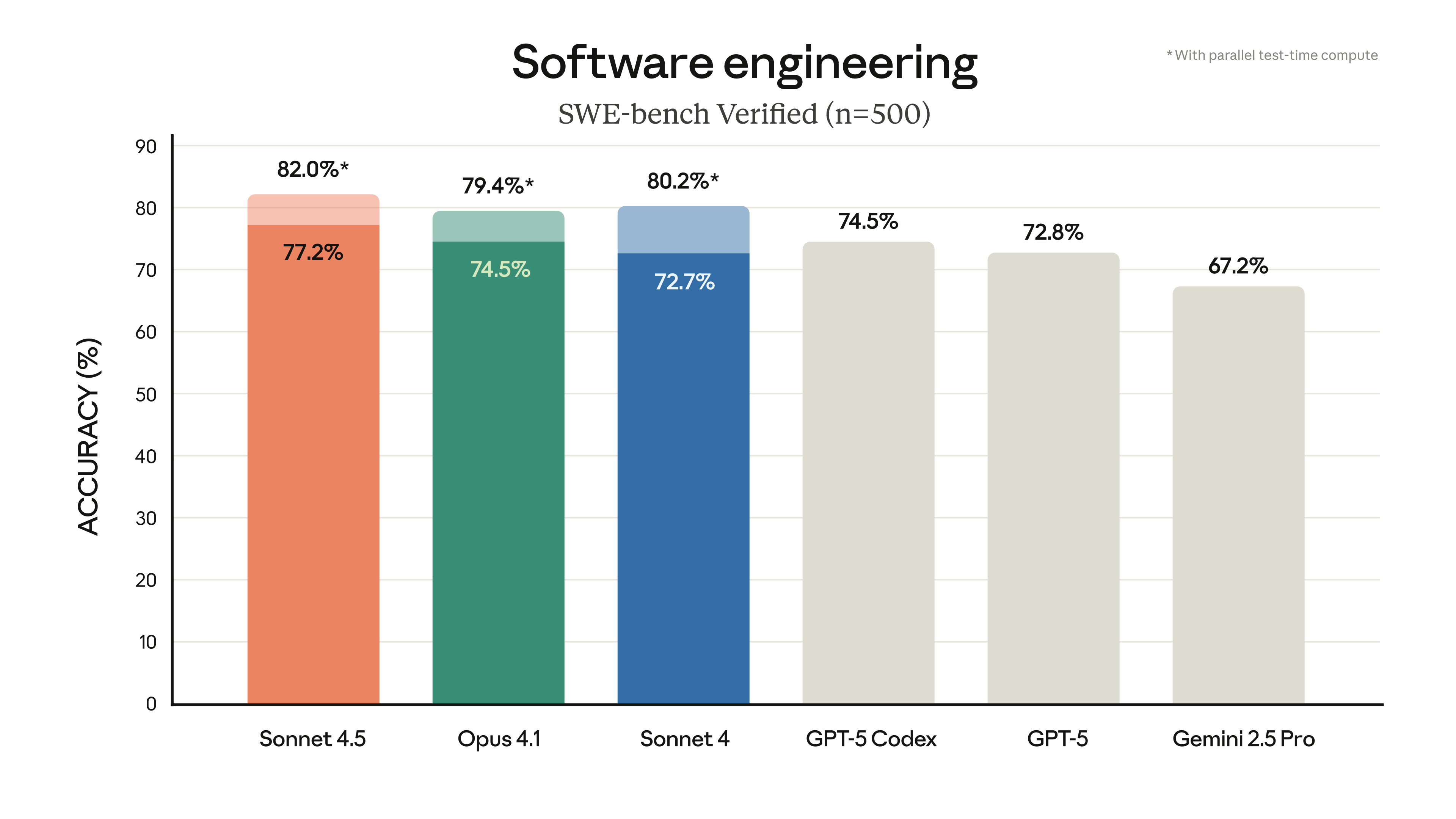
MIRIX is an innovative personal digital assistant system developed by a team from the University of California, San Diego and New York University. Unlike traditional personal assistants, it uses a multi-intelligent body architecture to realize six dimensions of memory management: core memory maintains the basic system functions, situational memory records the operation context, semantic memory handles the textual content, procedural memory stores the operation steps, resource memory manages the file locations, and knowledge base integrates external information. This design enables it to achieve an operation recognition accuracy of 85.381 TP3T in the LOCOMO benchmark test and a storage compression efficiency of 99.91 TP3T.
The system workflow consists of three phases: firstly, real-time recording of screen activities through the visual capture module; then conversion of raw data into structured memories by the information extraction engine; and finally construction of a searchable digital timeline. Typical application scenarios include: researchers tracking read academic papers, working professionals managing daily workflow, students building personal knowledge base, etc.
In terms of technical implementation, MIRIX adopts the Apache 2.0 open source license and supports all platforms of Windows/macOS/Linux. Its visual processing frequency is set to 1 frame per second by default, and it can run smoothly on 8GB RAM devices, which is friendly to users' hardware requirements.
This answer comes from the articleMIRIX: A Multi-Intelligent Personal Assistant for Intelligent Tracking of Screen ActivityThe