Fake News Detector is an automated fake news detection system based on fact checking. It utilizes artificial intelligence techniques, specifically Large Language Models (LLMs) and advanced embedding models, to analyze the truthfulness of news texts. Its core workflow is to first automatically identify and extract the core ideas or statements that need to be verified from the news content entered by the user. Then, the system will use a search engine to go to the Internet to find relevant evidential information. By comparing and analyzing the news statement and the searched evidence, the system will finally give a judgment on the authenticity of the news, such as "correct", "wrong" or "partially correct", and The system will finally give a judgment on the truthfulness of the news, such as "correct", "wrong" or "partially correct", and show the basis of judgment and reasoning process. The entire system is operated through a visual web interface, allowing users to see the progress of each step of the verification process intuitively.
Function List
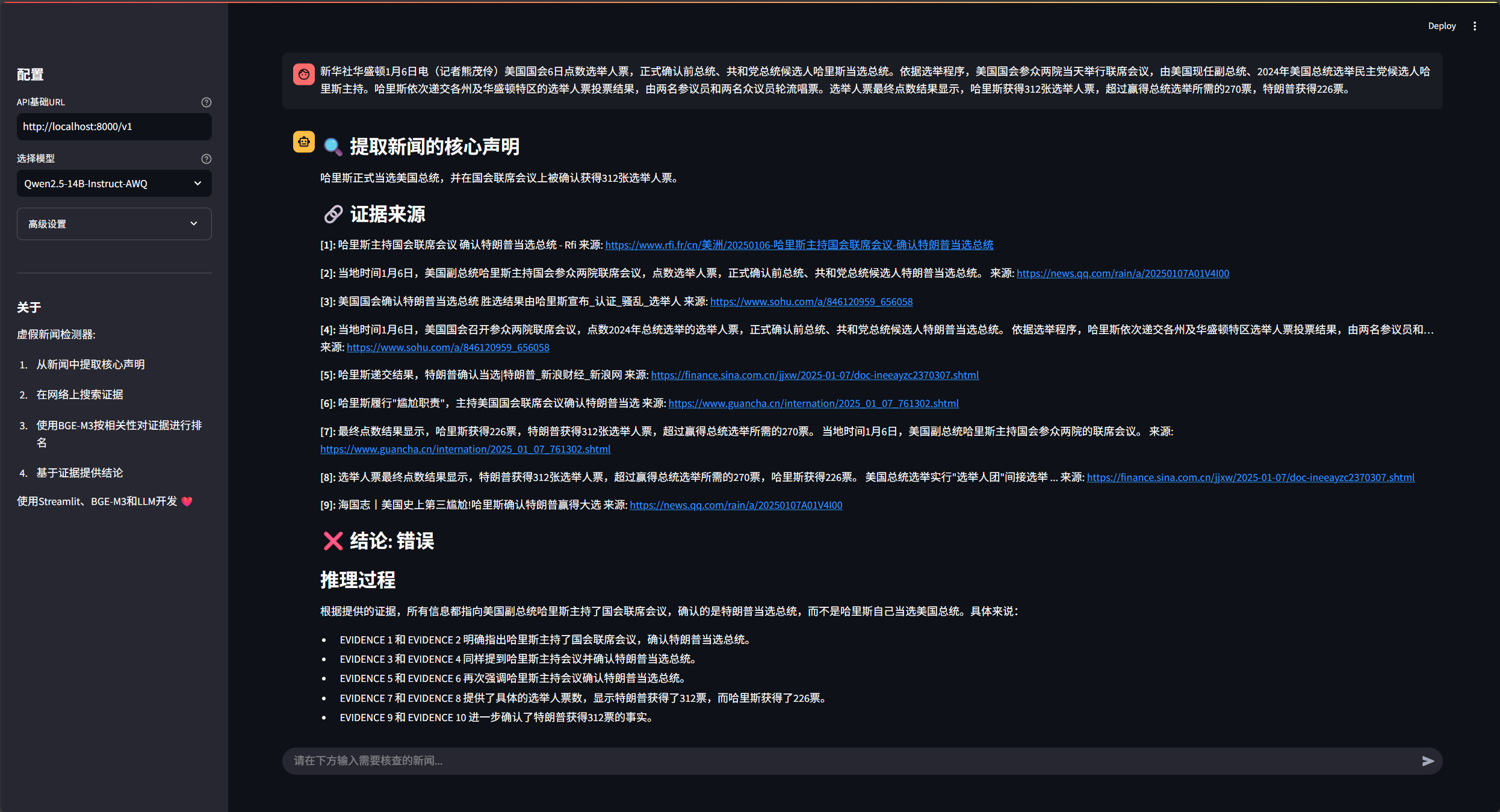
- Automatic extraction of core statements:: Automatically identifies and extracts the most critical core factual statements that need to be verified from complex news texts.
- Real-time web search:: The system is plugged into the DuckDuckGo search engine, which is capable of searching the Internet in real time for relevant articles, reports, etc. as supporting material based on the extracted core statements.
- Semantic Matching Analysis:: The BGE-M3 embedding model was used to compute semantic correlations between news statements and web evidence, ensuring that the evidence found was highly relevant to the content of the viewpoints to be verified.
- Long-text evidence processing:: When the searched evidentiary material is too long, the system automatically splits it into smaller paragraphs and filters out the pieces of evidence that are most relevant to the core statement.
- Reliable fact-checking:: Based on the evidence found, the system synthesizes and gives a verification conclusion of "correct", "incorrect" or "partially correct" and explains the reasoning process that led to the conclusion.
- Visualization Interface: Built a user-friendly web interface through Streamlit that allows users to see every step of the process in real time, from statement extraction, to evidence search, to final judgment.
Using Help
The tool is an application that needs to be deployed by the user on their own computer, it does not have a website that can be accessed directly, so some basic programming knowledge is required to complete the installation and launch.
preliminary
Before starting the installation, you need to make sure that your computer meets the following conditions:
- Installing Python: Your computer needs to have Python version 3.12 installed. You can find and download the installer from the Python website.
- Large Language Model (LLM): You need a large language model that can be deployed locally, for example
Qwen2.5, or any other model compatible with the OpenAI API interface. This is the core that drives the entire system for analysis and judgment. - embedding modelYou need to prepare
BGE-M3Embedded model, either downloaded from the web and deployed locally or called remotely via an API. This model is mainly used to analyze the similarity between texts.
Installation steps
- Clone Code Repository
First, you need to download the project's source code from GitHub to your computer using the Git tool. Open your computer's Terminal (Command Prompt or PowerShell on Windows, Terminal on macOS or Linux) and enter the following command:git clone https://github.com/CaptainYifei/fake-news-detector.gitAfter executing the command, the code will be downloaded to a file named
fake-news-detectorof the folder. Next, go into this folder:cd fake-news-detector - Installation of dependent libraries
Running the project relies on a number of third-party Python libraries, which are documented in therequirements.txtfile. You can use thepiptool installs all required libraries in one click. Run the following command in the terminal:pip install -r requirements.txtThis process may take some time as it will automatically download and install all the necessary software libraries.
- Configuring Model Paths
After the installation is complete, you need to tell the program yourBGE-M3Where the embedded model is stored.- Locate the project folder in the
fact_checker.pyfile and open it with a code editor. - Find the following line of code in the file:
self.embedding_model = BGEM3FlagModel('/path/to/your/bge-m3/') - Change the paths in the code to
'/path/to/your/bge-m3/'Modify it to store your ownBGE-M3The actual folder path of the model. If you are using a remote API, you will need to modify this part of the code according to the requirements of the model service provider you are using.
- Locate the project folder in the
launch an application
After all the configurations are done, you can start this fake news detection tool. In the root directory of the project (fake-news-detectorfolder), open a terminal and run the following command:
streamlit run app.py
After the command is executed, the program automatically opens a new page in your browser at the address that is usuallyhttp://localhost:8501. This is the interface of the tool.
How it works
Once the app launches, you'll see a clean web interface.
- Find a text input box on the interface.
- Copy and paste the complete text of the news item you want to verify authenticity into this input box.
- Click on "Start Verification" or a similar button.
- The system will start working immediately and you can see the verification process updated in real time on the interface, including:
- The core statement of the news is being extracted...
- Searching for relevant evidence...
- Evidence is being analyzed for relevance to the statement...
- Fact-checking conclusions are being generated...
- Finally, the system displays the final verification conclusion (correct, incorrect, or partially correct) with relevant links to the evidence and the analysis process to give you an idea of how it arrived at that conclusion.
application scenario
- Rapid screening of information by individual users
This tool can be utilized for quick fact-checking when an individual sees an uncertain news story on social media or the web. Users simply copy and paste the text of the news into the tool to get an initial judgment based on online evidence, helping them avoid being misled by rumors. - Journalist Aids
For journalists, editors and other news practitioners, this tool can serve as an efficient aid. Before reporting or quoting a piece of news, it can be used to carry out preliminary authenticity screening, quickly find relevant supporting materials or discover contradictions, thus enhancing the accuracy and rigor of news reporting. - Content platform information review
Social media platforms, content aggregation sites, and the like can integrate similar technologies to automate the review of large amounts of information on the platform. Through real-time analysis of content posted by users, potential false information can be quickly identified and flagged, reducing the scope of rumors and maintaining a healthy ecology of platform content.
QA
- What languages does this tool support for news detection?
The tool relies heavily on the capabilities of the Large Language Model (LLM) and embedded models behind it. Theoretically, if the configured models (e.g. Qwen2.5 and BGE-M3) support multilingual processing, then the tool is also able to process news texts in the corresponding languages. Currently, the main focus is on Chinese and English. - Are the test results completely reliable?
Not completely reliable. The tool's detection results are based on the AI model's search and analysis of publicly available information on the web, which can be used as a very valuable reference, but cannot be guaranteed to be 100% accurate. The accuracy of the results is affected by the quality of evidence that can be found by the search engine, as well as the judgment ability of the big language model itself. For the verification of very important information, users are advised to use the results of this tool as an aid, and to combine it with other channels to seek evidence from multiple sources. - I'm not a programmer, can I use this tool?
For users without programming background, it will be difficult to use the project directly because it requires code download, environment configuration and startup on a local computer. Currently, the project does not provide a public online website, and is mainly aimed at developers or researchers with a certain technical foundation.
































