Docstrange is an open source document processing tool that specializes in extracting data from documents and images in multiple formats and converting them to formats such as Markdown, JSON, CSV or HTML. It utilizes artificial intelligence and advanced OCR technology to support the processing of PDF, Word documents, Excel tables, PowerPoint presentations, images and web content. Users can quickly extract text, tables, or specific fields with simple code or command line operations, making it suitable for developers, researchers, and business users working with complex documents. The tool supports cloud and local processing, guarantees data privacy, and the output is well-structured, making it especially suitable for use with Large Language Models (LLMs).Docstrange is developed by NanoNets, hosted on GitHub, free, and easy to integrate.
Function List
- Extract text and data from PDF, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, images and web pages.
- Support for converting extracted content to Markdown, JSON, CSV, HTML and plain text formats.
- Provides intelligent field extraction to extract specific information based on user definitions, such as invoice numbers or contract terms.
- Supports JSON schema definitions and outputs data that conforms to a user-specified structure.
- Built-in advanced OCR technology to process text in images and scanned documents.
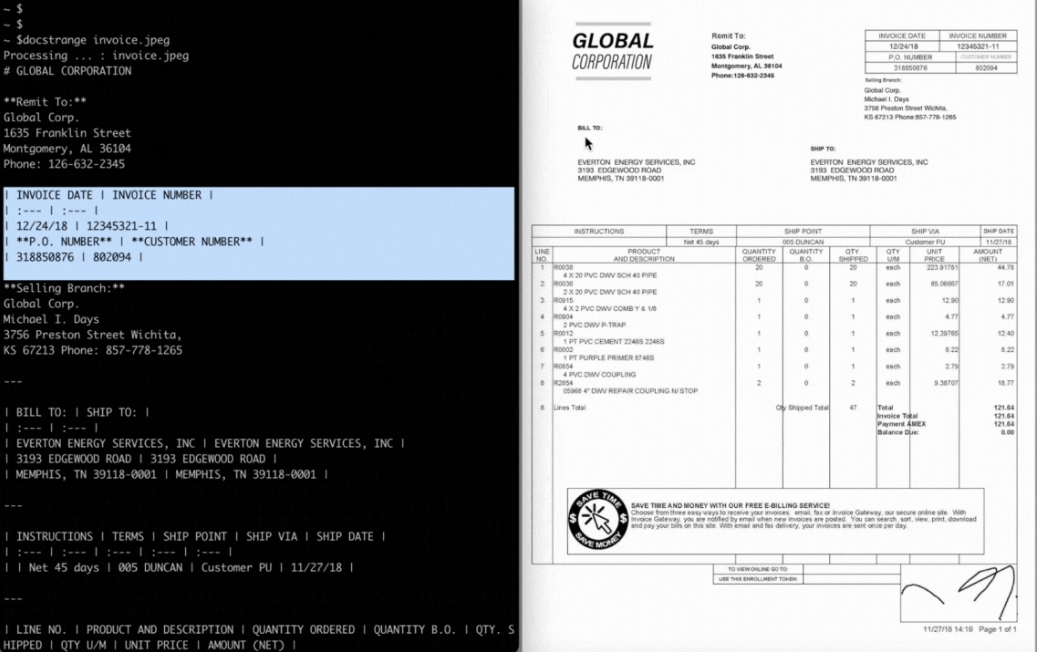
- Provides table extraction functionality that preserves the structure of complex tables and converts them to Markdown or HTML.
- Supports local CPU or GPU processing to protect data privacy.
- Provides both command line and Python API operation , suitable for developers to integrate .
- Supports batch processing of multiple files to improve work efficiency.
Using Help
Installation process
To use Docstrange, you first need to install the Python environment (Python 3.8 or above is recommended). Then install the Docstrange library by following these steps:
- Installing Docstrange
Run the following command in a terminal to install Docstrange:pip install docstrangeOnce installed, the user can invoke the tool from a Python script or from the command line.
- Get API key (optional)
If you are using cloud processing mode, you can register and get a free API key on the NanoNets website to increase the processing limit. After obtaining the key, you can pass the key in the command line via--api-key YOUR_API_KEYparameter is specified. - Local processing mode (optional)
If fully localized processing is required, install a dependency that supports native OCR (e.g. Ollama). Run the following command to enable CPU or GPU processing:docstrange document.pdf --cpu-mode或
docstrange document.pdf --gpu-modeNote: GPU mode requires a CUDA-supported hardware environment.
Usage
Docstrange offers two main ways to operate: the Python API and the command line. The following describes in detail how to use the core functionality.
Using the Python API
Docstrange's Python API is suitable for developers to integrate into existing projects. Here is an example of extracting the contents of a PDF file:
from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
# 初始化提取器(默认云端模式)
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
# 提取 PDF 文件并转换为 Markdown
result = extractor.extract("document.pdf")
markdown = result.extract_markdown()
print(markdown)
# 提取特定字段
fields = result.extract_data(specified_fields=["invoice_number", "total_amount"])
print(fields)
# 使用 JSON 模式提取结构化数据
schema = {
"contract_number": "string",
"parties": ["string"],
"total_value": "number"
}
structured_data = result.extract_data(json_schema=schema)
print(structured_data)
Users can choose the output format (Markdown, JSON, CSV, HTML) according to their needs. [](https://github.com/NanoNets/docstrange)
Used from the command line
Command line operations are suitable for quick processing of files. The following are some common commands:
- Extract PDF files and output to Markdown:
docstrange document.pdf --output markdown - Extracts specific fields and outputs them as JSON:
docstrange invoice.pdf --output json --extract-fields invoice_number total_amount - Batch processing of multiple PDF files:
docstrange *.pdf --output markdown - Save the results to a file:
docstrange document.pdf --output-file result.md
The command line supports flexible parameter combinations, and users can specify the output format or processing mode according to their needs.
Featured Function Operation
- Intelligent Field Extraction
Docstrange allows the user to specify the fields to be extracted, such as invoice number, amount or contract date. For example, when processing invoices:docstrange invoice.pdf --output json --extract-fields invoice_number vendor_name total_amountThe tool automatically recognizes relevant fields in the document and returns structured JSON data. This is ideal for scenarios where key information needs to be extracted quickly.
- Form Extraction
For documents containing complex tables, Docstrange can accurately extract the tables and convert them to Markdown or HTML format. For example:result = extractor.extract("financial_report.pdf") html_table = result.extract_html() print(html_table)The output form retains its original structure and is suitable for direct use in web pages or document editing.
- local processing mode
To protect data privacy, users can enable local processing mode:extractor = DocumentExtractor(cpu=True) result = extractor.extract("document.pdf") print(result.extract_markdown())Local mode eliminates the need to send data to the cloud and is suitable for sensitive document processing.
- JSON Schema Support
Users can define JSON schemas to ensure that the output data conforms to a specific structure. For example, processing contract documents:schema = { "contract_number": "string", "parties": ["string"], "total_value": "number", "start_date": "string" } structured_data = result.extract_data(json_schema=schema) print(structured_data)This approach is suitable for data output scenarios that require standardization.
caveat
- Cloud mode requires a stable internet connection and it is recommended to use an API key for faster processing.
- Native mode requires an additional OCR dependency to be installed, see the GitHub documentation for specific requirements.
- Currently the tool does not support the processing of handwritten documents and is suitable for processing printed or electronic documents.
application scenario
- academic research
Researchers can use Docstrange to convert PDF files of academic papers into Markdown format, preserving the table and text structure for further analysis or importing into a knowledge base. - financial management
Business users can extract key fields (e.g. amount, date) from invoices, receipts or financial reports and export them to JSON or CSV for easy import into financial software. - Legal Document Processing
Attorneys can quickly extract key clauses or signature information from contracts to generate structured data and streamline the contract review process. - data analysis
Data analysts can extract tables from web pages or Excel files into CSV format for data visualization or machine learning model training.
QA
- What file formats does Docstrange support?
It supports data extraction from PDF, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, images (PNG, JPG, etc.) and web page URLs. - How do you ensure data privacy?
Users can choose between local CPU or GPU processing modes, and data is not uploaded to the cloud, making it suitable for handling sensitive documents. - Do I have to pay to use it?
Docstrange is an open source tool and is free to use. Cloud mode requires registration of a NanoNets account for API keys, and free accounts have usage limits. - Can you handle handwritten documents?
Currently Docstrange mainly supports printed or electronic documents, with limited handling of handwritten documents.
































